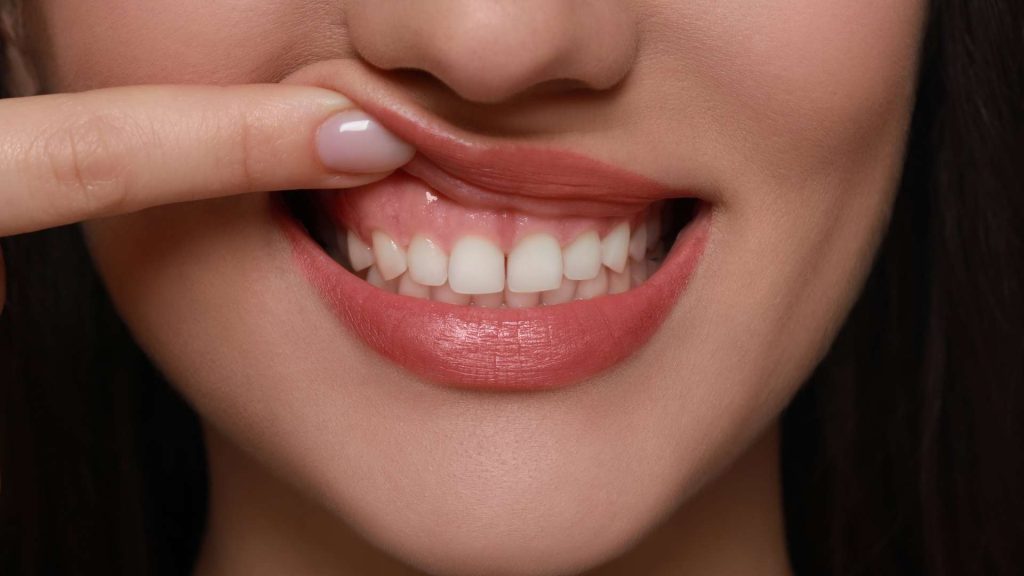
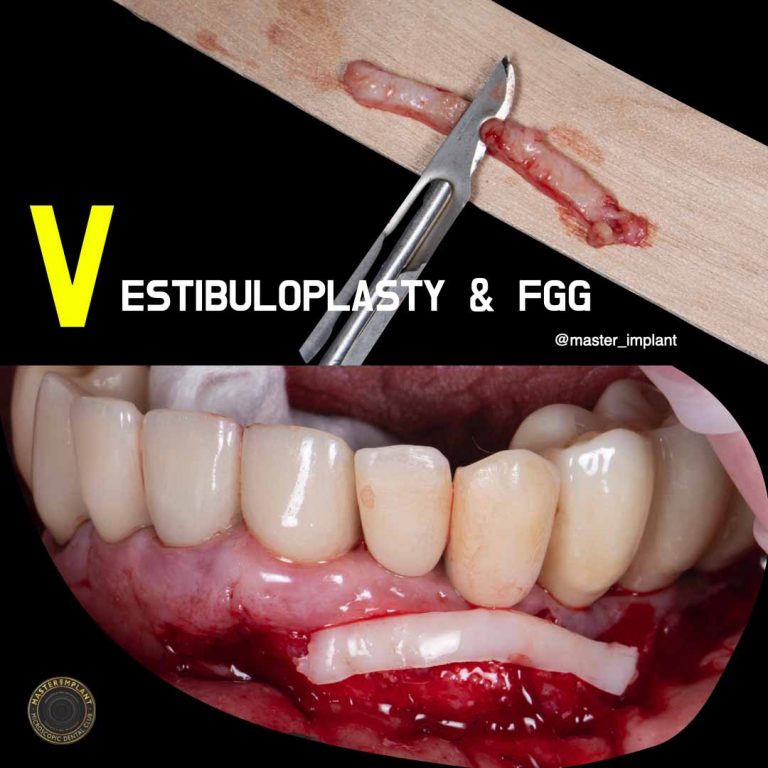
Gum grafting is a specialized dental procedure designed to treat thin gingival tissue or cases of gum recession. The gums play a fundamental role in overall oral function and dental health specifically. They are the soft tissue that surrounds the teeth and bone, protecting tooth roots while creating, together with the bone, the support system for our teeth.

When Receding Gums Threaten Your Smile
Gum recession or thin gingival lines can compromise the integrity of tooth roots, leading to cervical caries and even bone resorption. This is why maintaining healthy and intact gums is crucial at all times.
The Surgical Approach, Precision Meets Innovation
Gum grafting involves the precise placement of a small segment of new soft tissue in areas with insufficient gingival tissue. The graft is typically harvested from the palate using a minimally invasive approach under local anesthesia.
The tissue is then carefully sutured to the deficient gingival area, allowing the new tissue to cover exposed tooth roots, add volume to the gum line, help prevent further recession, and create a more aesthetically pleasing oral appearance.
Recovery and Healing
Recovery typically takes several days (thanks to cold laser therapy) to one week, though in specific cases it may extend longer. Gum grafting has high success rates when performed by skilled practitioners using advanced technology, including therapeutic microscopy, microsurgical instruments, and various laser types to accelerate the healing process.
Dr. Ariel Savion has been an active dentist since 2007 and holds a dual Master’s degree from Germany in Laser Sciences and Dental Implantology. He has clinical expertise in laser periodontal therapy, microscopic surgery, and dental implant procedures.
He serves as the Medical Director of the dental corporation Savion Medical Center Ltd. and is the founder and owner of the prestigious master_implant educational club, dedicated to training dentists in advanced fields of dentistry.
In addition, Dr. Savion is the only certified instructor in Israel on behalf of the World Clinical Laser Institute in the field of laser dentistry.
Dr. Savion is an international researcher and lecturer and serves as a Key Opinion Leader (KOL) for leading medical companies in Israel and worldwide, specializing in laser dentistry, periodontology, and dental implantology.

Clinical Benefits of Gum Grafting
Clinical Benefits
- Reduced risk of periodontal disease progression and tooth extraction
- Decreased risk of cervical caries due to exposed tooth roots
- Reduced pain and tooth sensitivity during eating or drinking
- Smile enhancement without root surface reduction (addressing root exposure from recession)
Clinical Indications for Gum Grafting
Several conditions warrant gum grafting surgery:
- Gum Recession and Root Exposure - This is the primary indication for gum grafting. When gingival tissue recedes, it exposes tooth roots and can lead to tooth sensitivity and increased risk of root caries. Gum grafting can serve as a "brake" to halt progressive recession and all its consequences.
- Advanced Periodontal Disease (Periodontitis) - This condition causes loss of gingival tissue, potentially requiring gum grafting both to restore gingival health and prevent disease progression and tooth loss.
- Tooth Sensitivity - Whether directly resulting from gum recession or other causes, increased tooth sensitivity affects patient quality of life. Gum grafting can cover exposed roots and alleviate sensitivity.
- Aesthetic Considerations - Some patients seek gum grafting to address uneven gum lines that affect oral appearance or to enhance smile aesthetics.
Recognizing the Signs of Gum Recession
The early stages of gum recession are relatively difficult to detect, but over time symptoms emerge:
- Teeth appearing longer due to root exposure, altering smile aesthetics
- Increased tooth sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, disrupting eating and drinking
- Uneven, notched gum lines along the margins where gums meet teeth
- Gum redness and swelling
- Tooth mobility due to compromised supporting gingival tissue and bone
- Gingival bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Following root scaling or surgical periodontal procedures
Treatment Modalities, Tailored Approaches for Optimal Outcomes
Several types of gum grafts exist, each serving specific purposes. The main differences lie in the tissue source and the specific condition they address:
Pedicle Graft – In this approach, tissue is taken from nearby gums (connective tissue) close to the tooth requiring treatment. This method is only suitable for patients with adequate gingival tissue in the treatment area.
Free Gingival Graft – A technique where gingival tissue is harvested from the patient to create keratinized gums around implants or in areas with thin gingiva. Provides better protection around crowns or roots. Recovery is fast and painless, thanks to cold laser treatment.
Connective Tissue Graft – An effective method for treating gum recession using palatal tissue from the patient. Helps cover exposed roots and increase gingival thickness, with the advantage of continued thickening over time. Recovery is rapid thanks to cold laser treatment with minimal pain.
Fibrin Graft – Fibrin-rich plasma extracted from patient blood that accelerates healing and promotes new blood vessel formation. Laser Advantage: Enables precise incisions, reduces infection risk, and improves tissue healing. The combination of fibrin and laser contributes to grafting success through precise placement and faster recovery.
Mucoderm Graft – An alternative collagen-based material derived from porcine skin that replaces human tissue and serves as a foundation for tissue regeneration. Advantage, High biocompatibility, natural appearance, encouragement of blood vessel and tissue growth, and reduced complication risk. Limitations, Infection risk, high cost, and sensitivity to porcine-derived materials.
Emdogain Treatment, Biological Enhancement
Emdogain is an organic material containing 90% amelogenin (protein), applied in gum grafting surgeries to promote gingival tissue regeneration.
During gum grafting surgery, the dentist applies Emdogain directly to exposed root surfaces. This helps stimulate regeneration of lost gingival tissues. The proteins in Emdogain assist with cell attachment, new tissue formation, and even bone regeneration.
Ultimately, they support reattachment of gingival tissue to the tooth root. The use of Emdogain in gum grafting has been proven to improve success rates of these treatments. Emdogain is considered a safe treatment.
Laser Technology: Revolutionizing Gum Grafting
Laser-assisted gum grafting represents the most advanced technique available today when performed by skilled, laser-certified dental practitioners, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods:
- The primary benefit of laser gum grafting is minimal pain. Many patients report feeling no pain during the procedure.
- Lasers cauterize blood vessels while cutting, reducing oral bleeding during and after grafting.
- Laser precision allows highly controlled and accurate tissue removal while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Certain lasers have antibacterial properties, sterilizing the surgical site and reducing infection risk.
- Laser incisions typically result in minimal scarring and better aesthetic outcomes.
- Lasers enable precise, gentle gingival tissue contouring to achieve desired aesthetic results.
- Laser-integrated procedures reduce post-operative discomfort and pain compared to traditional techniques. Lasers promote faster, more efficient soft tissue healing by reducing inflammation and encouraging collagen production. Laser work requires less local anesthesia.
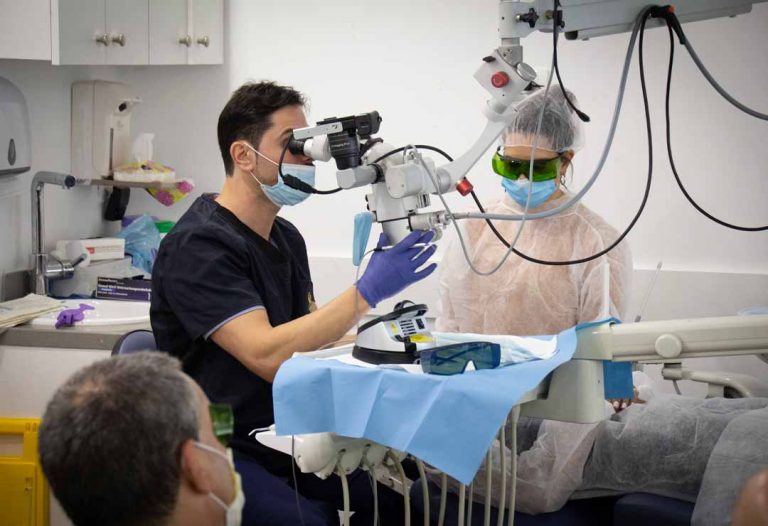
Microscopic Excellence, Enhancing Success Through Precision
Integrating dental microscopy into dental treatments has proven revolutionary, significantly improving success rates across various dental procedures. Through substantial magnification and clear illumination of the diagnosed or treated oral area, dental microscopy reveals complex details and anatomical structures with exceptional clarity and precision.
This enhanced visualization translates to more accurate diagnoses, precise treatment planning, and meticulous procedure execution. Whether performing complex root canal treatments, sophisticated oral rehabilitation, or delicate periodontal procedures, the improved visibility provided by microscopy enhances the dentist's ability to identify and treat problems that might otherwise remain undetected.
Furthermore, the improved precision and control afforded by microscopy enables complex microsurgical interventions with minimally invasive approaches, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues and better preserving healthy tooth structure. Ultimately, integrating microscopy into dental treatment elevates treatment and healing quality, contributing significantly to overall dental treatment success.
Risk Assessment, Potential Complications
Gum grafting procedures are generally considered safe, especially when performed by experienced dental practitioners. However, like any surgical medical procedure, several potential complications may occur:
- Infection risk exists, as with any surgical procedure
- Pain, discomfort, and swelling are common effects that are typically temporary
- Graft failure can occur when the graft doesn't integrate properly with existing tissues
- Graft rejection may appear when inappropriate tissue is used
- Excessive gingival tissue growth, though this is a rare occurrence
Post-Surgical Care, Recovery and Integration
Following gum grafting surgery, proper oral care is essential to ensure smooth healing and recovery. During this period, new blood vessels grow into the graft and help it integrate with surrounding tissue.
Each individual's healing process is unique, making it vital to follow the dentist's specific instructions and guidelines. Several key considerations can accelerate and improve recovery:
- Dietary Management – Adhere to soft, non-spiced, and non-acidic foods during the initial days post-surgery. Gradually reintroduce regular foods only after consulting with your dentist.
Oral Hygiene Protocol – Rinse with lukewarm salt water to keep the area clean. Brush gently near the surgical site, avoiding the grafted area during the first few days. Always follow your dentist's specific post-operative oral hygiene instructions.
- Pain Management –Some pain and discomfort are common following gum grafting surgery. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be used, though it's preferable to consult with your dentist regarding the recommended medication type.
- Activity Restrictions – Avoid strenuous physical activity during the first few days post-surgery to prevent increased bleeding. Refrain from smoking, as it can impede healing and increase complication risk.

Selecting Your Specialist
Choosing the right dentist for your gum grafting procedure is a serious matter aimed at ensuring successful, trauma-free treatment. Several evaluation criteria can guide your selection:
Seek recommendations from friends, family, or healthcare professionals. Personal experiences can provide valuable insights into a particular dentist's treatment quality.
Look for a dentist who has completed all necessary specializations for advanced grafting procedures. Is he current with the latest techniques and developments in the field? For example: Does he utilize dental microscopy and dental lasers in treatment? And more.
Schedule a consultation with the dentist to discuss your specific needs and treatment options. This opportunity allows you to assess their communication skills and those of the clinic staff:
Are they empathetic, attentive, and prepared to address your concerns? Are they willing to answer questions? How comfortable do you feel?
Important! Don't underestimate the value of a second opinion; it's crucial to find a practitioner who provides a sense of comfort and attentiveness.
Dr. Ariel Savion, Advanced Credentials in Periodontal Grafting
Dr. Ariel Savion recognizes the paramount importance of knowledge in general and professional expertise specifically, of continuous updates with all scientific and technological innovations in dentistry, and uncompromising professional work.
Dr. Savion holds an M.Sc. in Oral Implantology (dental implants) from Frankfurt University, Germany. In addition to his dental implant specialization, he holds an M.Sc. in Laser Sciences in Dentistry from Aachen University, Germany, as well as a BOARD CERTIFIED DIPLOMATE in dental implants from the international implantology organization ICOI.
Dr. Savion holds a global MDC degree in Microscopic Dentistry and Microsurgery, integrating microscopy in dental implants, gum grafting, and more, using minimally invasive approaches. He serves as a board member of the prestigious global MICROSCOPIC DENTAL CLUB, which promotes the integration of microscopy in dental treatments.
Thanks to Dr. Savion's extensive knowledge and experience in grafting and laser-microscopy dental treatments, he is considered a sought-after lecturer domestically and internationally in dental aesthetics, implantology, and microsurgical dentistry integrating microscopy and lasers.
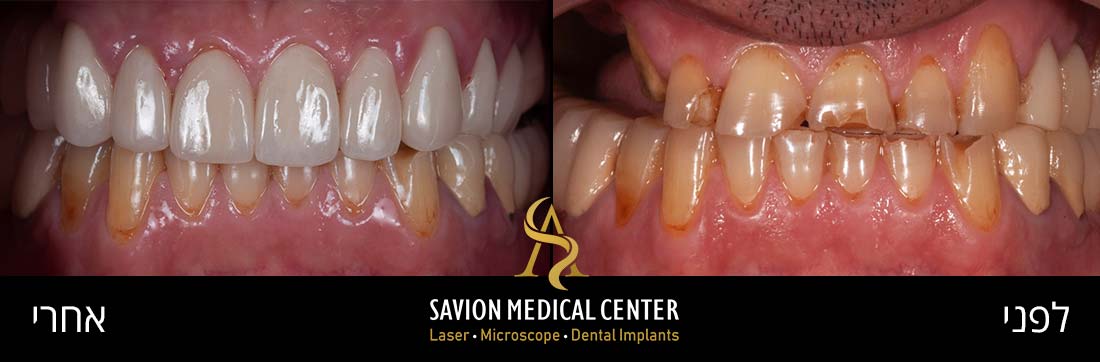
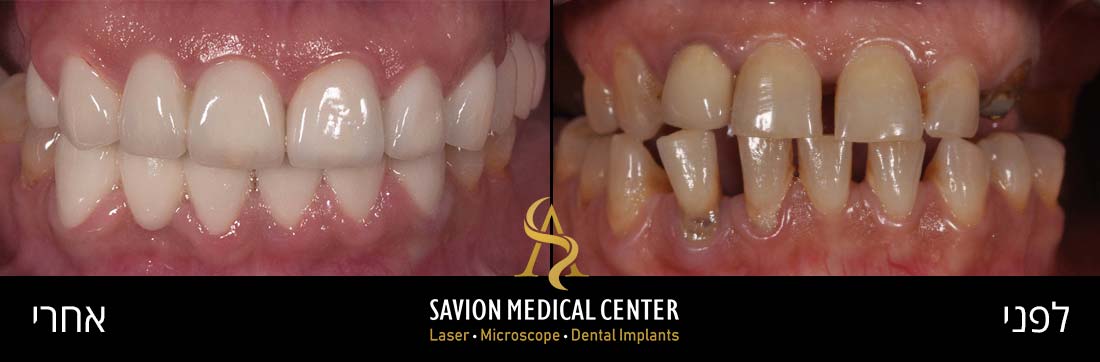
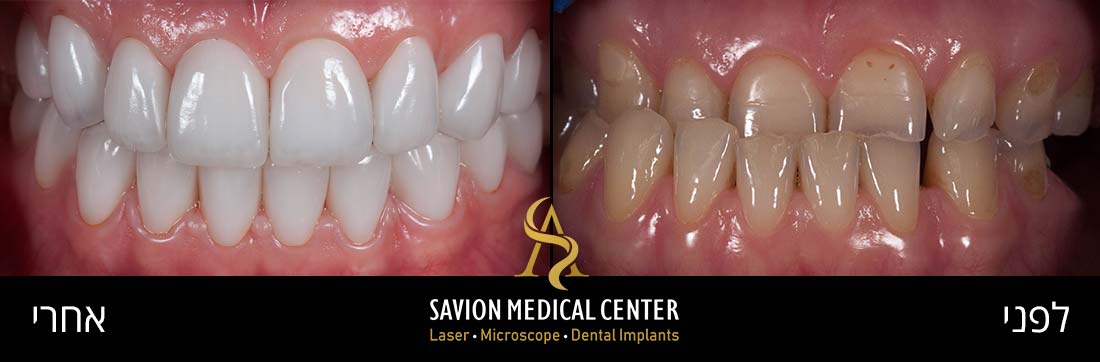
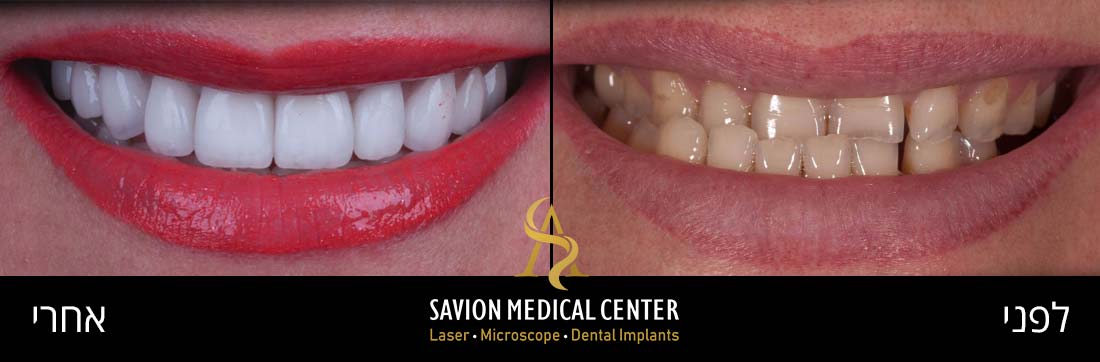
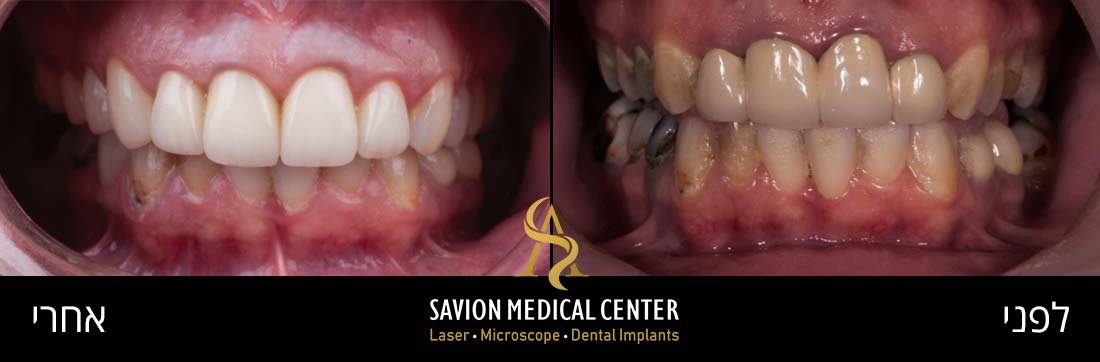
Gum grafting - before and after photos
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Grafting
Gum grafting is recommended for cases of gum recession, advanced periodontal disease, tooth sensitivity due to root exposure, or aesthetic needs to improve gingival appearance.
Risks include infections, temporary pain, bleeding, and rarely, graft failure. Selecting an experienced practitioner reduces risk.
The procedure involves grafting new gingival tissue in tissue-deficient areas, typically by harvesting a graft from the palate. Treatment is performed under local anesthesia.
Recovery lasts several days to a week, depending on case complexity. Laser use may accelerate the healing process.
Yes, successful gum grafting can provide a permanent solution and reduce the risk of recurrent gum recession.