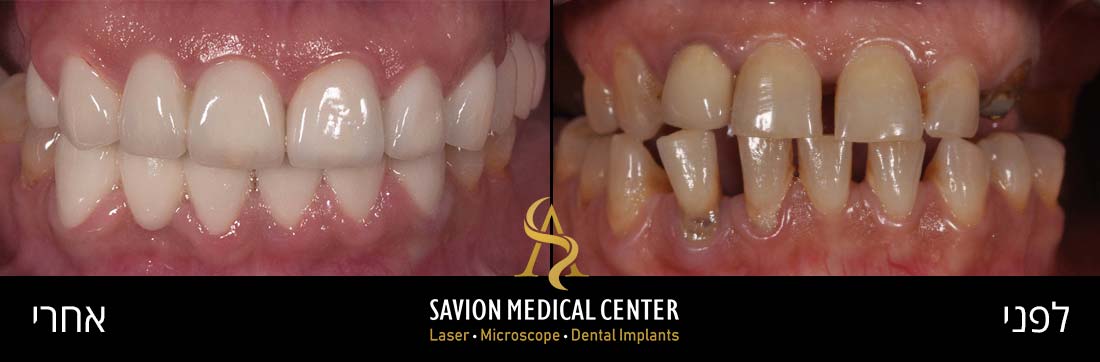
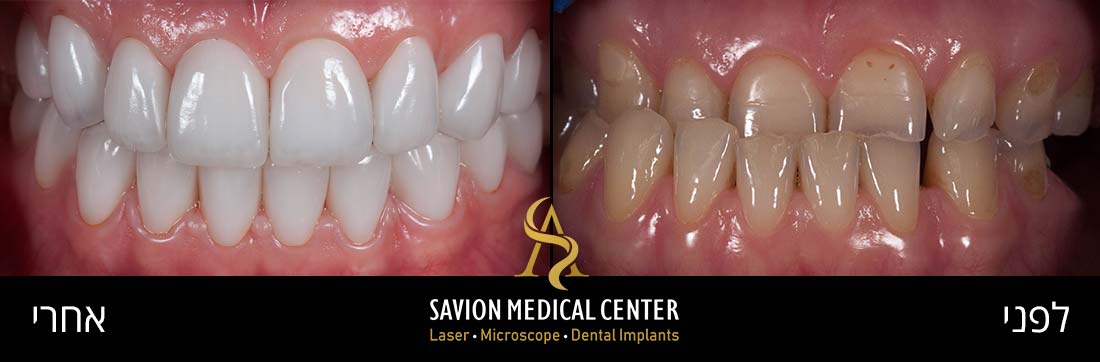
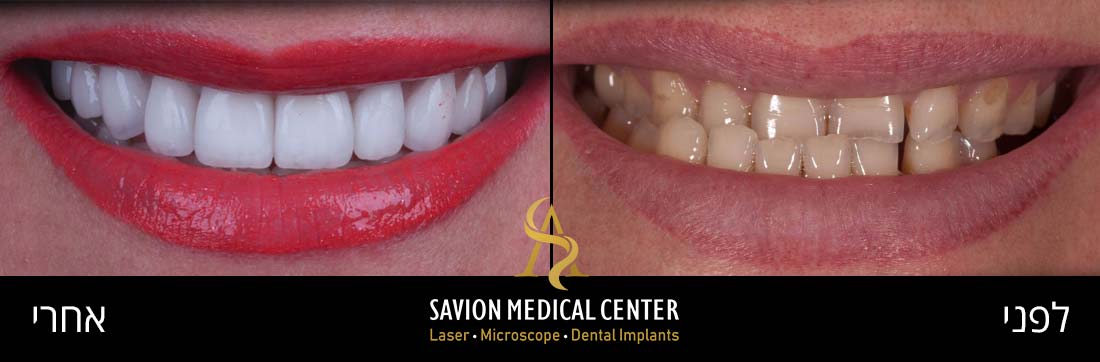
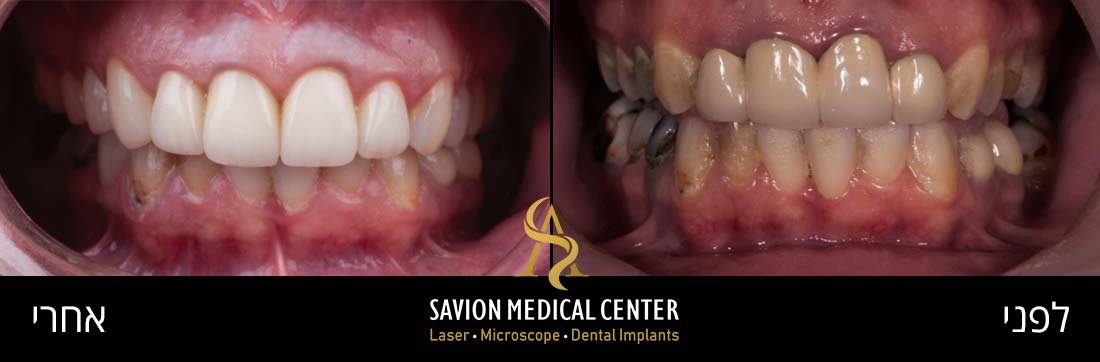
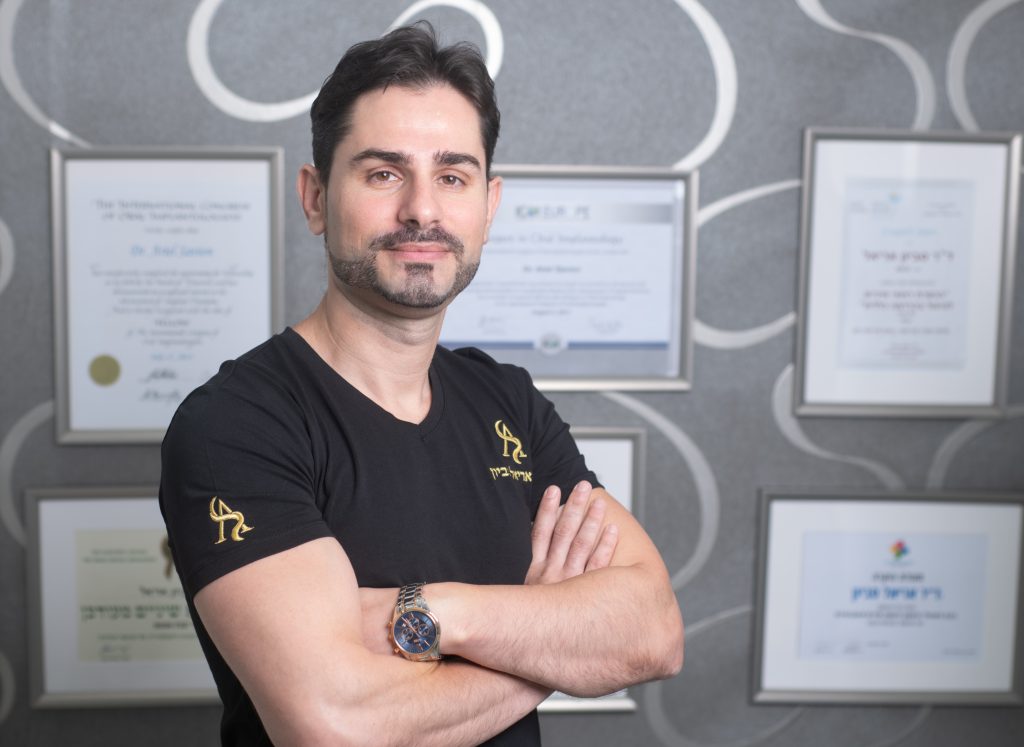
Mild Gum Pain
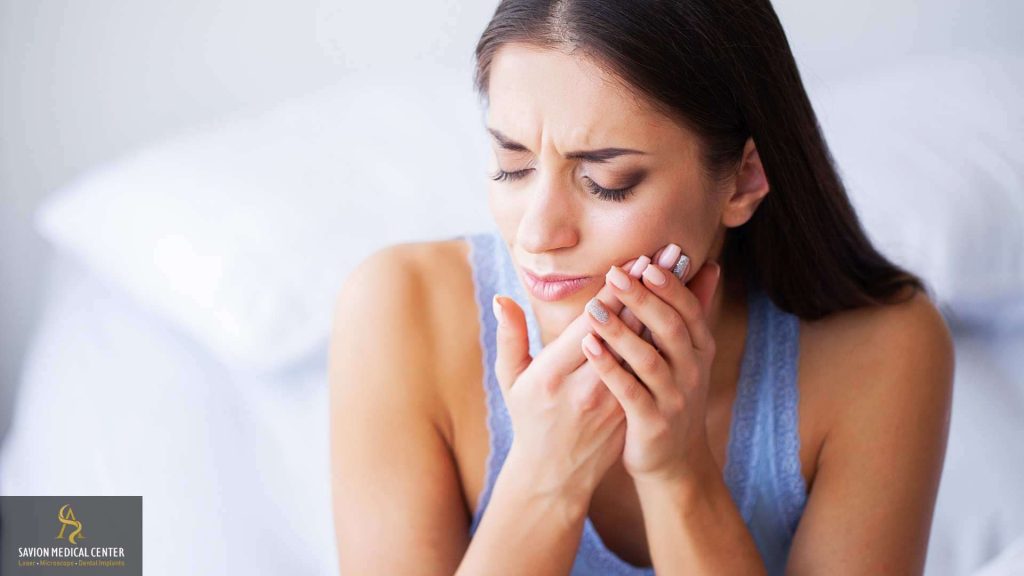
Gum pain is a very common condition experienced by people of all ages. Mild discomfort may arise from simple issues such as trapped food particles between the teeth or a minor gum infection. In many cases, this pain is temporary and does not necessarily require a dental visit.
Mild gum pain can feel like a persistent, dull ache or occasionally appear as sharp pain that subsides with proper oral hygiene. It is important to distinguish mild gum pain from more severe pain, which may indicate a deeper problem. If discomfort persists, worsens, or is accompanied by swelling, bleeding, or signs of infection, it is essential to seek prompt dental care.
Dr. Ariel Savion has been an active dentist since 2007 and holds a dual Master’s degree from Germany in Laser Sciences and Dental Implantology. He has clinical expertise in laser periodontal therapy, microscopic surgery, and dental implant procedures.
He serves as the Medical Director of the dental corporation Savion Medical Center Ltd. and is the founder and owner of the prestigious master_implant educational club, dedicated to training dentists in advanced fields of dentistry.
In addition, Dr. Savion is the only certified instructor in Israel on behalf of the World Clinical Laser Institute in the field of laser dentistry.
Dr. Savion is an international researcher and lecturer and serves as a Key Opinion Leader (KOL) for leading medical companies in Israel and worldwide, specializing in laser dentistry, periodontology, and dental implantology.

Managing Severe Gum Pain
Severe gum pain often indicates an underlying issue that requires immediate attention. It may be caused by advanced gum disease, the development of an abscess, or a significant infection. Patients describe this pain as constant, sometimes throbbing, and in some cases radiating to the jaw or other areas of the face.
Severe gum pain can interfere with basic activities like eating, speaking, and sleeping. Treatment depends on the cause and may include:
- Professional Cleaning
Removal of plaque, tartar, and bacteria to ease inflammation.
- Medication
Prescribed antibiotics to fight infection and pain relievers for symptom management.
- Advanced Treatments
In severe cases, procedures such as root planing, gum grafting, or periodontal surgery may be necessary to restore gum health.
Relieving and Soothing Gum Pain
When gum pain is mild or temporary, simple at-home measures can provide relief.
Home Remedies
Rinsing with warm salt water can help reduce swelling and soothe irritated gums. Cold compresses applied externally to the cheek near the affected area may also alleviate discomfort. Over-the-counter pain-relieving gels, particularly those containing benzocaine, can provide temporary numbing.
When to Seek Professional Care
If home remedies and non-prescription treatments do not bring relief or if pain worsens, consulting a dentist is essential. A dentist can prescribe stronger pain medication or anti-inflammatory drugs. In cases involving infection, abscesses, or gum disease, professional cleaning, disinfection, or even minor surgical procedures may be required to address the underlying cause.
Common Causes of Gum Pain
- Trapped Food Particles - Debris lodged between teeth can irritate the gums, with pain usually resolving after thorough cleaning with floss.
- Gingivitis - Early gum inflammation marked by redness, swelling, and bleeding, often caused by plaque and tartar buildup. Prompt and consistent oral hygiene can reverse this stage.
- Advanced Periodontitis - If untreated, gingivitis may progress to chronic gum disease involving infection that affects the gums and underlying bone. This condition often causes persistent pain and can eventually lead to tooth loss. Treatment includes deep cleaning, root planing, anti-inflammatory medications, and, in some cases, surgery.
- Abscesses and Infections - Severe, sharp pain may indicate pus buildup at the root of a tooth or between the gums and teeth. Such cases require urgent dental intervention for drainage and antibiotic therapy.
- Hormonal Changes - Pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can increase gum sensitivity and cause temporary discomfort. Proper oral care and, if necessary, over-the-counter pain relief can help manage these symptoms.

Risk Factors That Exacerbate Gum Pain
Several factors increase the likelihood or severity of gum pain:
- Poor oral hygiene leading to plaque buildup and inflammation
- Smoking, which reduces blood flow and impairs healing
- Diabetes, which heightens gum sensitivity and infection risk
- Genetic predisposition, making some individuals more prone to gum disease
- Medications that cause dry mouth, creating an environment favorable to infections
Gum Pain Following Dental Procedures
It is common to experience temporary gum discomfort after dental treatments such as fillings, extractions, or professional cleanings. This type of pain is typically a natural response to the instruments’ contact with the gums and surrounding tissues rather than a sign of a complication.
To relieve this discomfort, patients can rinse with warm salt water, use antibacterial mouthwash, apply cold compresses to reduce swelling, or take over-the-counter pain medication. If pain persists beyond several days or worsens, it is important to return to the dentist to rule out infection or other issues requiring further treatment.

Could Gum Pain Mean I Have Gum Disease?
Gum pain can indeed be an early sign of gingivitis. Common accompanying symptoms include gum redness, swelling, bleeding during brushing, and increased sensitivity. However, gum pain can also stem from other conditions, such as abscesses or oral ulcers.
A professional dental evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis. Early treatment helps prevent the condition from worsening and reduces unnecessary discomfort.
Gum Pain in Children: What Does It Mean?
While gum pain in children often causes concern among parents, it is frequently related to minor, non-serious causes such as teething, mild injuries from accidental bites, or brushing too hard. Poor brushing habits can also lead to gum inflammation in children.
If the pain is accompanied by swelling, bleeding, or does not subside, consulting a pediatric dentist is recommended to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
How to Prevent Gum Pain
The good news is that gum pain can often be prevented with consistent care:
- Brush teeth regularly and properly, using floss to remove debris between teeth.
- Use antibacterial mouth rinses to reduce harmful bacteria.
- Maintain a balanced, healthy diet while limiting foods that damage teeth and gums.
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke, both of which significantly increase the risk of gum disease.
- Schedule routine dental check-ups for early detection of gum and dental problems.

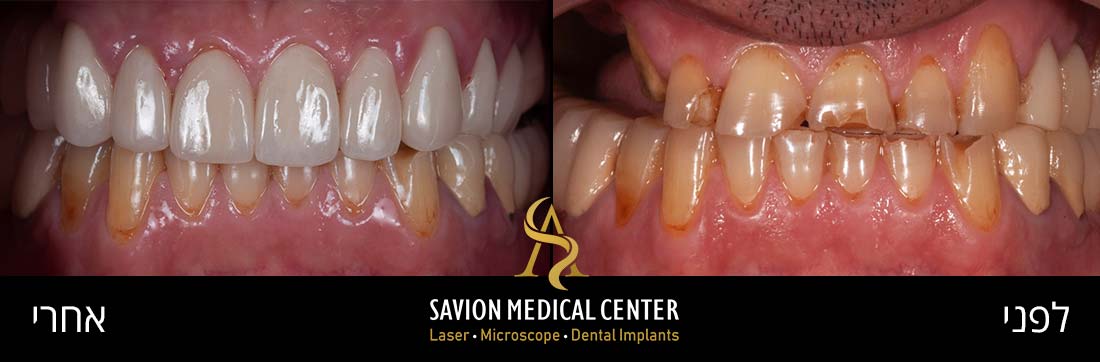
Gum Care at Savion Medical Center
Are you experiencing gum pain whether mild or severe? Concerned about possible gum disease or infection? At Savion Medical Center, led by Dr. Ariel Savion, we specialize in diagnosing and treating all types of gum pain, periodontal diseases, and performing restorative and implant dentistry.
Our clinic provides a full range of treatments from professional cleanings and preventive care to advanced laser therapies and surgical procedures when needed. Don’t wait for mild discomfort to escalate into significant pain. Contact Savion Medical Center for evaluation and take the first step toward healthier, pain-free gums.