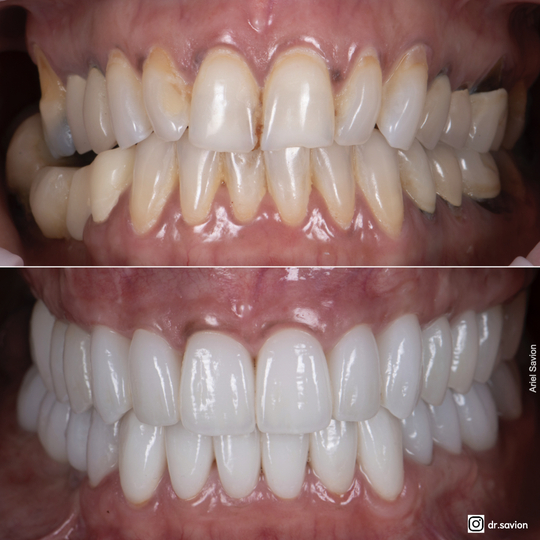
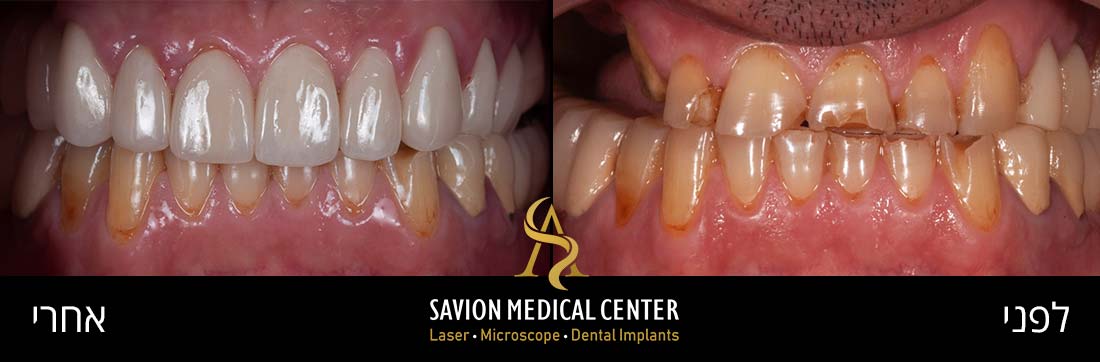
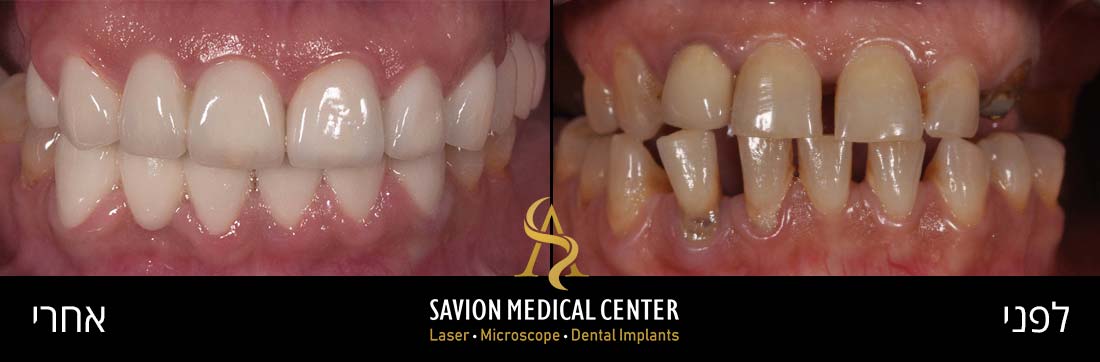
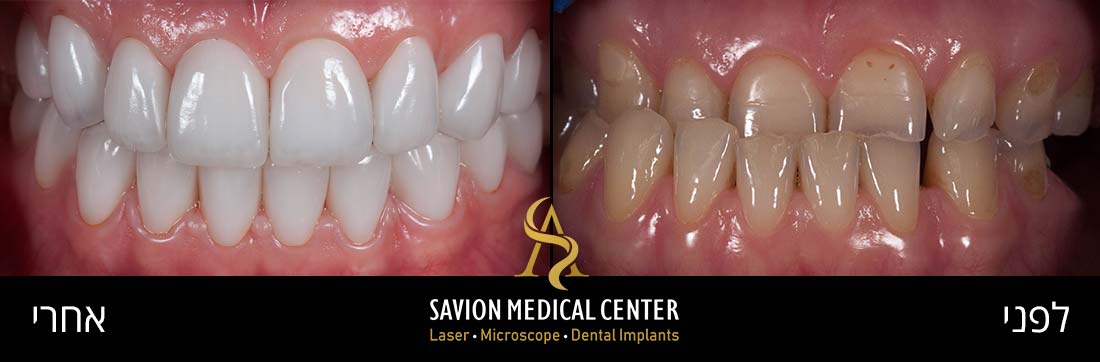
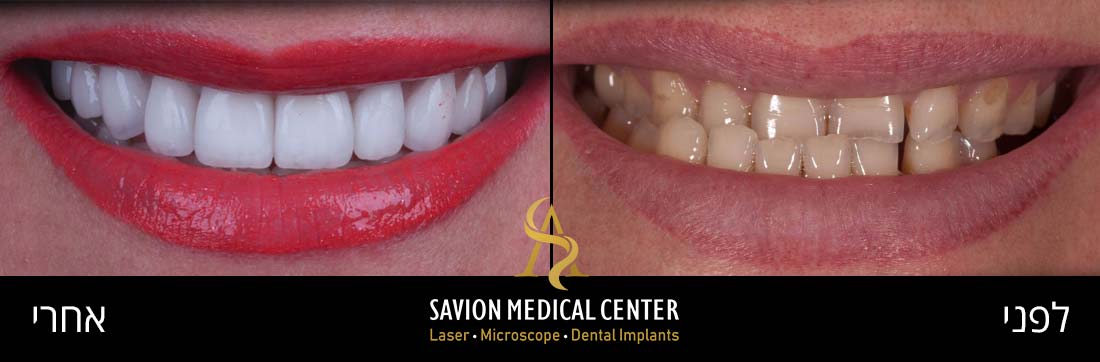
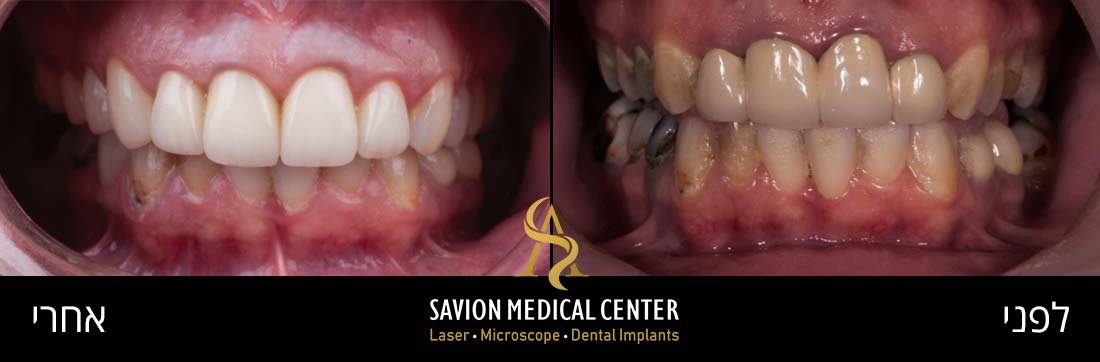
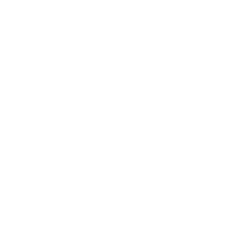
- The Causes of Tooth Discoloration
Common Causes of Tooth Staining:
- Childhood trauma to primary teeth – Impact to baby teeth can damage the developing permanent tooth beneath, often resulting in white "scar-like" spots when the permanent tooth emerges.
- Excessive fluoride exposure – While fluoride strengthens teeth against decay, high concentrations during childhood can cause brown discoloration (fluorosis).
- Dental caries – This bacterial disease affects tooth enamel, typically beginning as white spots that progress into brown or yellow cavities.
- Calculus buildup – Bacterial plaque that hardens over time becomes tartar, which absorbs pigments from food, beverages, and tobacco.
- Poor oral hygiene – Inadequate brushing in both adults and children leads to orange-tinted staining from food debris and bacterial accumulation.
- Systemic conditions – Diseases such as celiac disease and gastroesophageal reflux can contribute to discoloration.
- Long-term dental bridgework – Can compromise effective tooth cleaning, leading to staining.
- Certain medications – Antibiotics like tetracycline can cause permanent discoloration when taken during tooth development.
- Aging – Natural wear and thinning of enamel over time.
- Genetic factors – Hereditary predisposition to tooth discoloration.
Dr. Ariel Savion has been an active dentist since 2007 and holds a dual Master’s degree from Germany in Laser Sciences and Dental Implantology. He has clinical expertise in laser periodontal therapy, microscopic surgery, and dental implant procedures.
He serves as the Medical Director of the dental corporation Savion Medical Center Ltd. and is the founder and owner of the prestigious master_implant educational club, dedicated to training dentists in advanced fields of dentistry.
In addition, Dr. Savion is the only certified instructor in Israel on behalf of the World Clinical Laser Institute in the field of laser dentistry.
Dr. Savion is an international researcher and lecturer and serves as a Key Opinion Leader (KOL) for leading medical companies in Israel and worldwide, specializing in laser dentistry, periodontology, and dental implantology.

Types of Tooth Stains
Tooth discoloration manifests in various colors, each indicating different underlying causes:
- Brown or yellow stains – The most common type, typically caused by consuming coffee, tea, or regular tobacco use.
- Gray or white stains – Usually result from calculus accumulation and poor oral hygiene.
- Black or dark brown stains – Often indicate decay or cavities requiring immediate treatment to prevent progression.
- Red or orange stains – May result from excessive consumption of berries, tomato-based sauces, or sports drinks.
- Blue or gray stains – Can be caused by certain antibiotics (such as tetracycline) taken during tooth development.
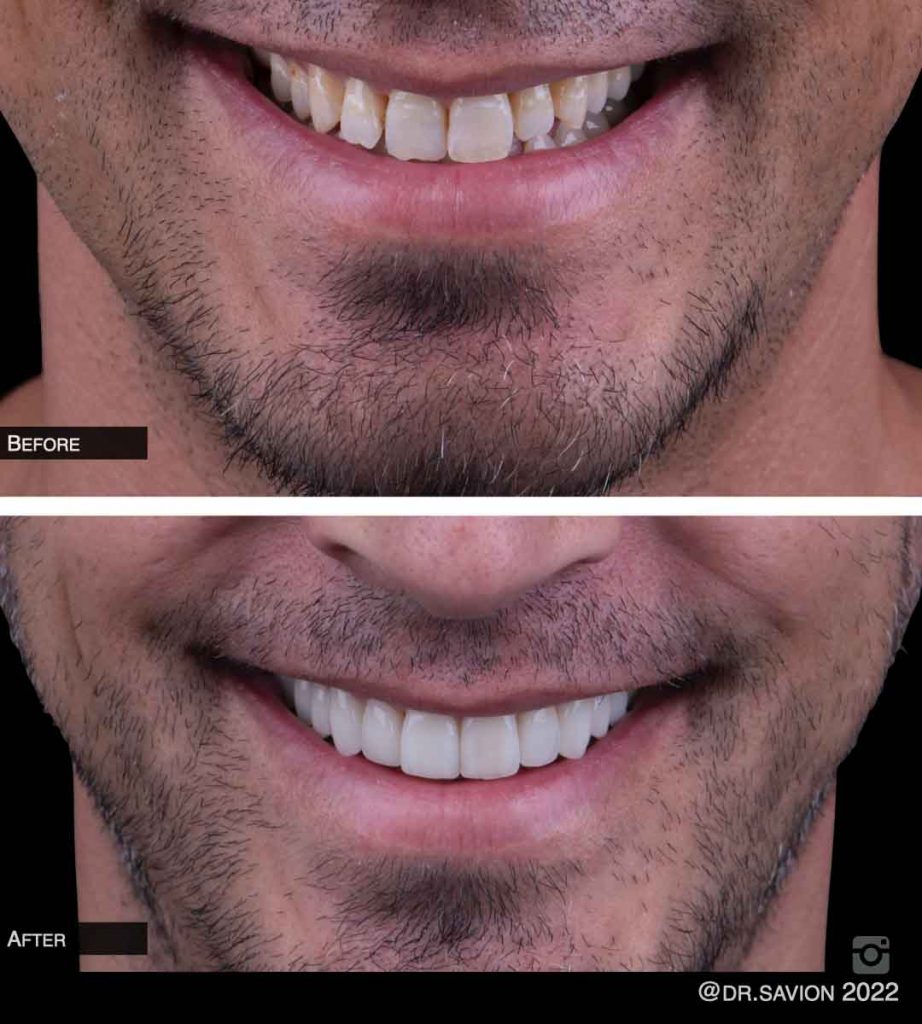
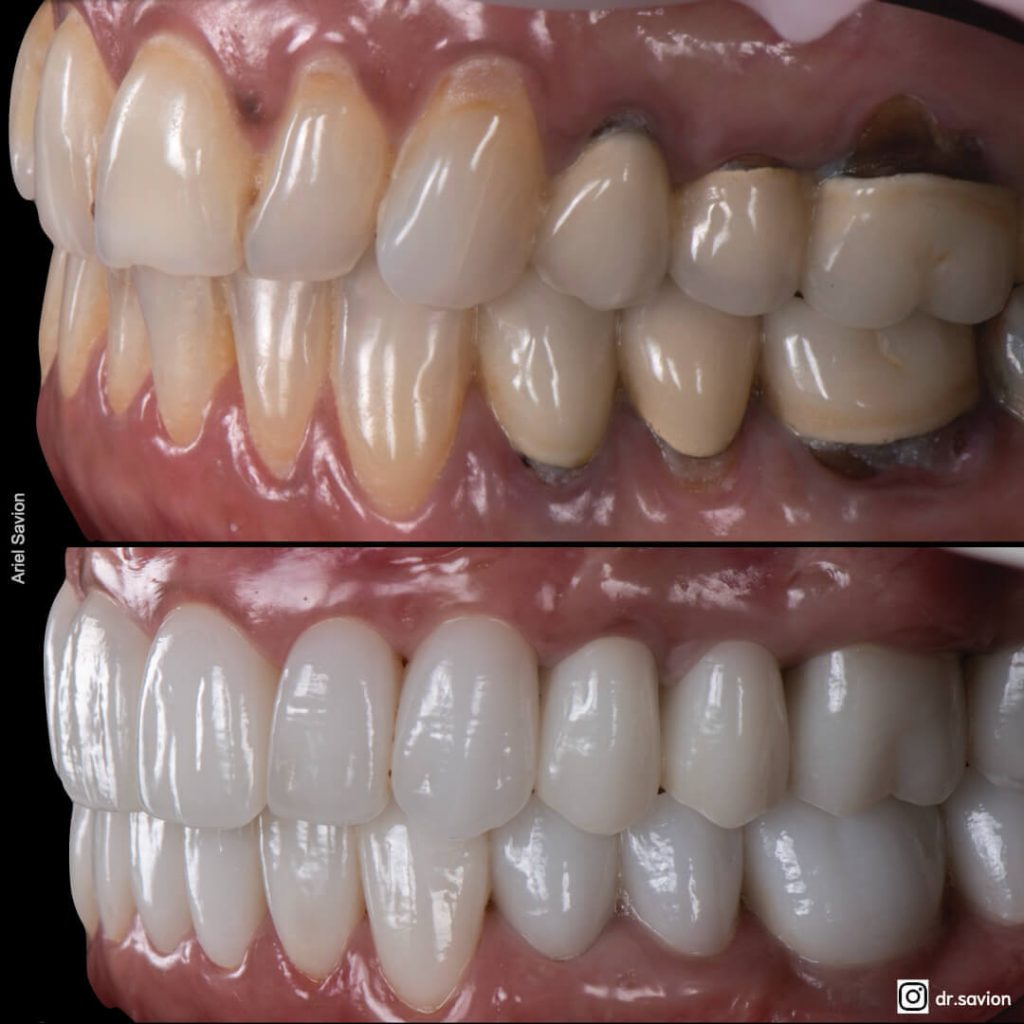
Professional Treatment Solutions for Tooth Stains
| Treatment Method | How does it work? |
| Micro abrasion (Chemical Polish) | Removes the thin enamel layer containing stains |
| Air Abrasion and Calculus Removal | High-pressure particle stream removes debris and surface stains |
| Composite Bonding (No Tooth Reduction) | Application of tooth-colored resin directly to tooth surfaces |
| Porcelain Veneers (0.3mm thickness) | Ultra thin ceramic shells precisely placed on tooth surfaces to cover imperfections |
- Micro abrasion (Chemical Polish)
Micro abrasion is a dental treatment designed to remove surface stains and discoloration. This technique combines gentle acidic agents with abrasive materials to eliminate the thin enamel layer containing the stains.
The Procedure – The process involves applying an acidic gel or paste to the tooth surface, which helps dissolve the outermost enamel layer. The gel is then gently polished into the teeth, removing the stained enamel. This process repeats until the desired whiteness is achieved.
Important Considerations – Micro abrasion isn't effective for all stain types and may be unsuitable for patients with significant enamel erosion or sensitivity. Results may not match the whitening achieved through other treatments like veneers or crowns.
Micro abrasion offers a safe, effective option for mild to moderate staining – a relatively quick and affordable treatment completed in a single dental visit.
- Air Abrasion and Calculus Removal
Air abrasion uses specialized equipment to spray fine particles (typically aluminum oxide or sodium bicarbonate) onto tooth surfaces. The high pressure particle stream effectively removes surface debris and staining, as well as calculus buildup. This process is also known as prophylaxis treatment.
Procedure – Often combined with calculus removal from teeth and gums, these procedures work together to clean and restore teeth to their natural appearance.
Important Considerations – Air abrasion may not suit all patients, particularly those with weakened enamel or sensitive teeth, as the abrasive particles could cause additional damage.
Additionally, it may prove ineffective for certain stain types, such as those caused by specific medications or medical conditions. When performed by a skilled dentist, air abrasion can effectively remove surface stains and clean teeth.
- Composite Bonding (No Tooth Reduction)
Composite bonding is a cosmetic dental procedure involving the application of tooth-colored resin to tooth surfaces. This procedure improves the appearance of stained, discolored, chipped, or gapped teeth.
A key advantage of composite bonding is its non-invasive nature – no tooth structure requires removal, unlike other cosmetic procedures such as certain veneers or crowns.
Procedure – The process involves roughening the tooth surface, applying a bonding agent, then applying the tooth-colored composite resin. The dentist then sculpts and polishes the material to match surrounding teeth for a natural appearance.
Benefits of Composite Bonding:
- Non invasive – requires no enamel removal
- Color-matched to patient's natural teeth for seamless results
- Quick and straightforward procedure
- Affordable, making it attractive for many patients
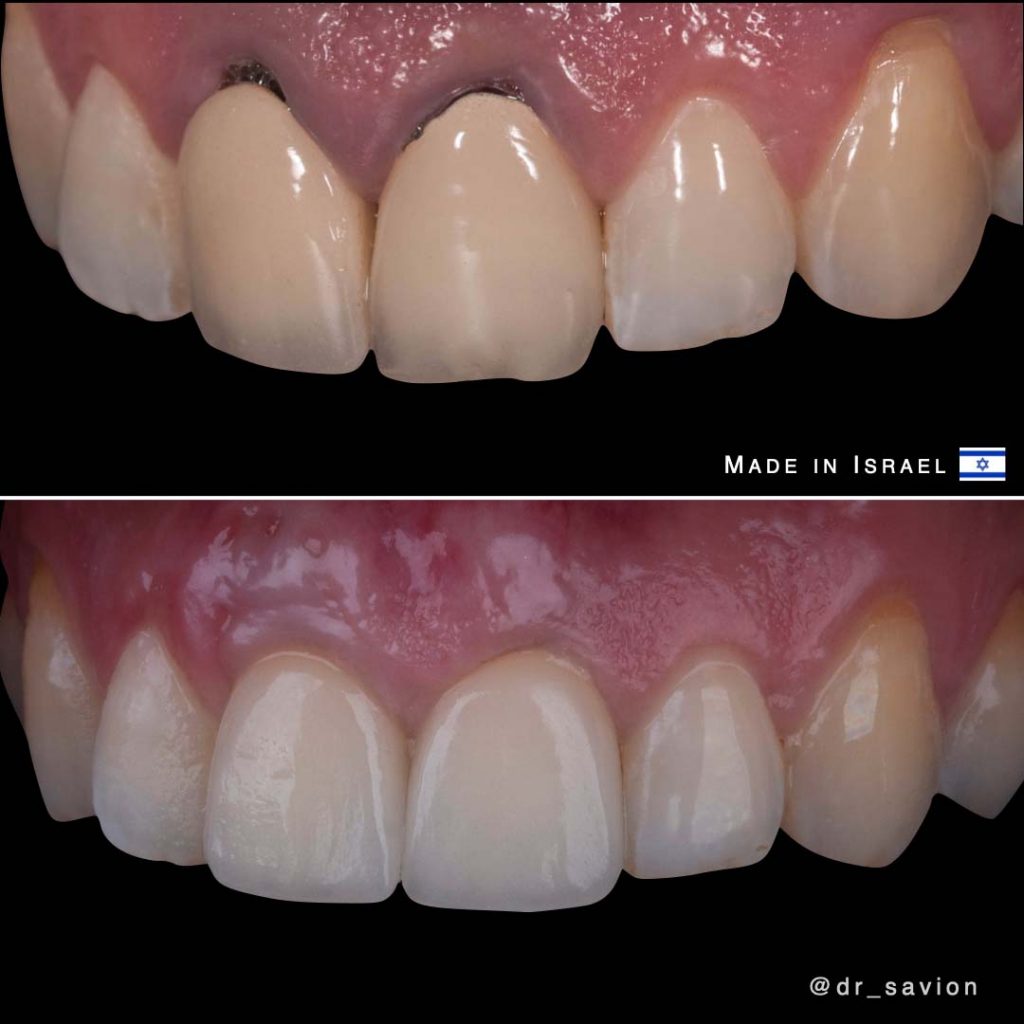
- Porcelain Veneers (0.3mm thickness)
Porcelain veneers are a popular cosmetic treatment for improving the appearance of stained, discolored, or chipped teeth. These ultra-thin ceramic shells are precisely placed on the front tooth surfaces to cover imperfections.
Why 0.3mm Porcelain Veneers Work for Stain Treatment:
- Custom matched – Veneers are individually crafted and color-matched to existing teeth.
- Durability – Porcelain is strong and withstands normal wear, providing a long-lasting solution.
- Stain-resistance – Porcelain resists staining, ensuring patients maintain a beautiful, white smile without worrying about future discoloration.
Preventing Tooth Stains
Effective Prevention Strategies:
Regular visits allow dentists or hygienists to remove calculus and debris that cause staining.
Antiseptic rinses help eliminate bacteria that contribute to discoloration.
Smoking and tobacco products cause severe staining and discoloration.
Brush twice daily and floss once daily to remove food particles and bacterial accumulation.
Foods and drinks containing pigments, coffee, tea, red wine, and berries, can cause staining. Reducing consumption or rinsing with water afterward helps prevent discoloration.
While "teeth whitening" is the common term for stain removal, it's important to understand the process actually brightens tooth enamel.
Three Professional Whitening Methods:
- At home whitening – The dentist creates a custom tray containing active whitening agents for the stained enamel. Patients wear the tray 1-2 hours daily for approximately 2 weeks to several weeks, depending on the case. The concentration and strength of the active agent is customized for each patient.
- In-office laser whitening – Performed exclusively by a dentist. The dentist applies an active whitening agent and uses laser activation in three 20-minute sessions. The entire process takes approximately 90 minutes. This offers fast, convenient, and effective results.
- Combined approach – For stubborn stains, combining in-office laser treatment with at-home whitening trays may be necessary to achieve desired results.
Over-the-counter whitening toothpastes and home kits contain minimal active ingredients, making their effectiveness limited.
Important Note! Address any existing dental issues – cavities, gum disease, or other oral health concerns – before pursuing stain removal treatment.

Microscope Enhanced Dentistry for Stain Removal
Microscopic dentistry utilizes high-powered microscopes with specialized lighting systems that magnify the oral cavity up to 39 times, dramatically improving visibility and enabling precise work during dental procedures.
This approach proves particularly valuable for complex procedures including periodontal surgery, dental implants, root canal treatment, and problematic wisdom tooth extraction, as well as calculus removal, subgingival root planing, crown placement, and tooth stain removal.
Fluorescence Guided Stain Removal:
Efficient stain removal can be achieved using fluorescence lighting under a treatment microscope. A special dye or solution containing fluorescent molecules is applied to tooth surfaces. When exposed to fluorescence lighting, this highlights and emphasizes tooth stains, allowing the dentist to locate and remove them with greater precision.
Fluorescence lighting also helps identify areas invisible to the naked eye – stains located in grooves or fissures that are difficult to detect without magnification. The combination of a dental microscope with fluorescence lighting enables more effective identification and treatment of these areas.
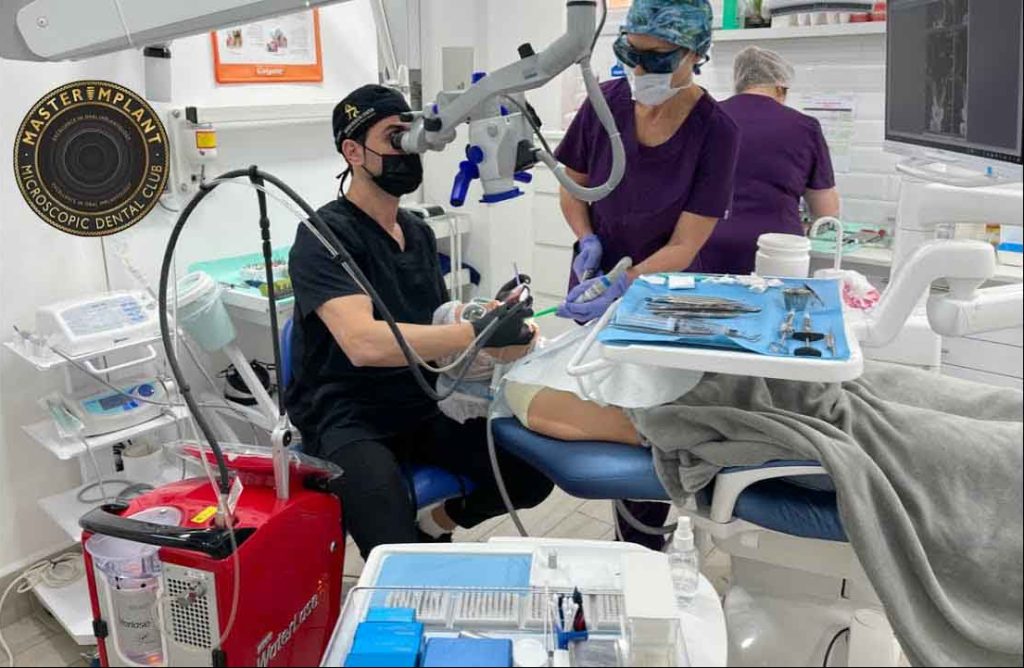
Benefits of Dental Microscopy in Stain Removal
Dental microscopy optimizes and enhances cosmetic dental procedures. It facilitates direct aesthetic restorations under magnification – for example, precisely restoring a tooth with coronal destruction so accurately that root canal treatment may be avoided.
Microscopic dentistry plays a crucial role in delivering precise, minimally invasive, and efficient dental care, ensuring optimal oral health for patients.
Dentists trained in microscopic techniques can work with exceptional precision and efficiency, ultimately achieving superior treatment outcomes.

When to Consult a Professional
Consult a dentist about tooth stain removal when:
- Stains persist despite regular oral hygiene practices (brushing, flossing, interdental cleaners)
- Discoloration darkens over time
- Staining accompanies other symptoms such as sensitivity, pain, or swelling
When uncertain whether tooth stains are normal, always consult a dentist. They can determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can stain removal treatments damage teeth?
While micro abrasion and air abrasion are generally safe, they may not suit individuals with weakened enamel or tooth sensitivity. Composite bonding and porcelain veneers don't harm teeth and provide long-term solutions for improving appearance.
Can crowns or veneers be whitened?
Crowns and veneers cannot be effectively whitened because they're made from materials that don't respond to whitening treatments – acrylic, porcelain, or zirconia. If teeth beneath crowns or veneers appear darker than surrounding teeth, ask your dentist to brighten them before placement, or request color-matching to adjacent teeth.
How do I know which treatment is right for me?
Consult a dentist who will perform a thorough examination and assess your teeth's condition and specific needs. Some situations may require one treatment over others for optimal results.
What's the difference between teeth whitening and stain removal?
Stain removal focuses on eliminating external stains using techniques like microabrasion or air abrasion. Teeth whitening uses bleaching agents to improve the overall tone of all teeth.
Is stain removal treatment painful?
Most stain removal treatments involve no pain. However, individuals with sensitive teeth may experience mild discomfort during treatment.
Are there side effects to stain removal treatment?
Potential side effects include temporary tooth or gum sensitivity following treatment. Following your dentist's post-treatment instructions helps minimize these effects.