Gum Disease and Why It Matters
Gum disease, or gingivitis, is one of the most common oral health conditions, affecting people of all ages. It may not always cause severe pain, but it should never be ignored. Left untreated, it can progress to advanced periodontal disease, leading to tooth loss and other serious complications.
The gums are the soft tissue that surrounds the base of the teeth, forming a protective seal. When the gums become inflamed or infected, problems such as bleeding, gum recession, and chronic infections often follow. Early detection and treatment are crucial, which is why regular dental check-ups are highly recommended for everyone.
Dr. Ariel Savion has been an active dentist since 2007 and holds a dual Master’s degree from Germany in Laser Sciences and Dental Implantology. He has clinical expertise in laser periodontal therapy, microscopic surgery, and dental implant procedures.
He serves as the Medical Director of the dental corporation Savion Medical Center Ltd. and is the founder and owner of the prestigious master_implant educational club, dedicated to training dentists in advanced fields of dentistry.
In addition, Dr. Savion is the only certified instructor in Israel on behalf of the World Clinical Laser Institute in the field of laser dentistry.
Dr. Savion is an international researcher and lecturer and serves as a Key Opinion Leader (KOL) for leading medical companies in Israel and worldwide, specializing in laser dentistry, periodontology, and dental implantology.

table of contents
The Main Causes of Gum Inflammation
The likelihood of developing gum inflammation increases with age, but there are several contributing factors at any stage of life. These include:The likelihood of developing gum inflammation increases with age, but there are several contributing factors at any stage of life. These include:
Elevated stress levels affect the immune system, making gums more susceptible to infection.
Hormonal changes can heighten gum sensitivity and inflammation.
compromises gum health and slows healing.
Certain blood pressure medications can increase gum inflammation.
Diabetes and other systemic diseases can weaken the body’s ability to fight gum infections.
Failure to remove plaque and tartar creates an ideal environment for bacteria.
Although gum disease is rare in children, bleeding during brushing or other symptoms should be taken seriously, as they can sometimes indicate health concerns that require evaluation.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Getting an Accurate Diagnosis
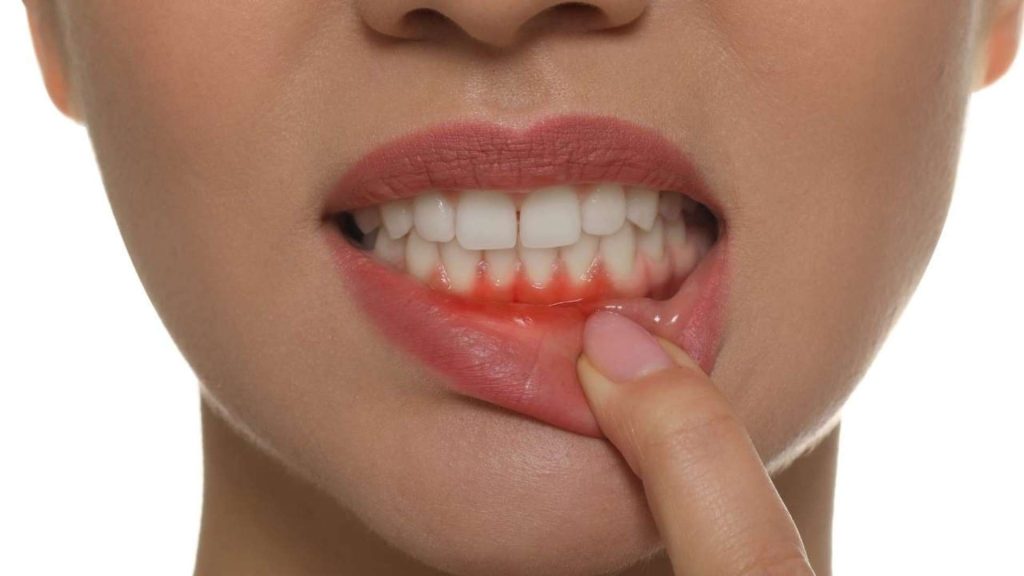
In its early stages, gum disease often causes little or no discomfort, making it easy to overlook. However, neglecting these early signs allows the disease to progress into periodontitis, a more advanced condition that can destroy the bone supporting the teeth. This leads to loosening of teeth, shifting in their position, and, in severe cases, tooth loss.
Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Gum recession, creating the appearance of “longer” teeth
- Teeth that feel loose or change position
- Persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Pus or discharge around the gum line
- If you notice deep pockets forming between your teeth and gums, or gaps at the gum line, it’s important to see a dentist immediately.
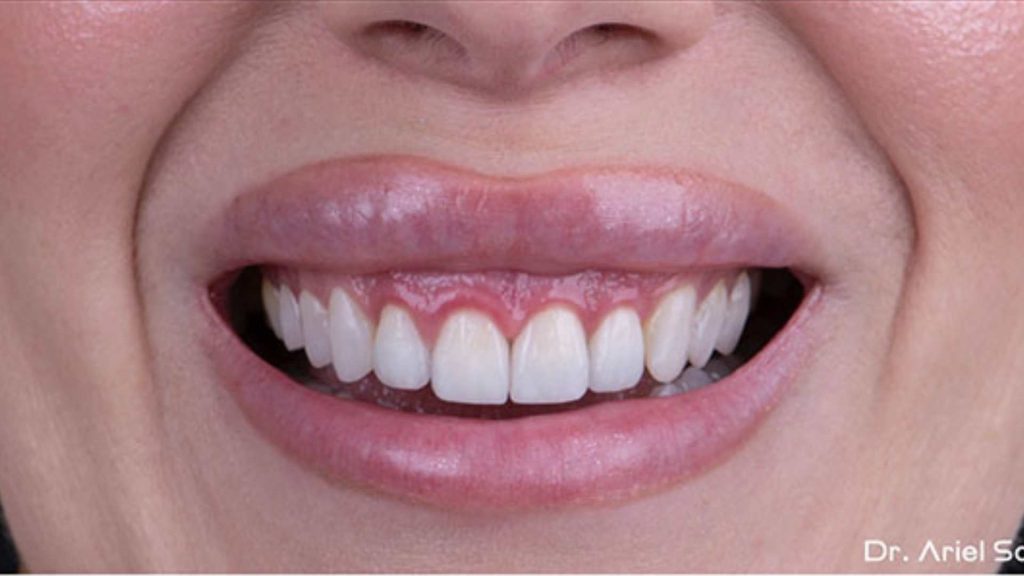
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
Treatment begins with a comprehensive periodontal evaluation. A periodontist performs a full mouth X ray assessment to evaluate bone levels, detect tartar buildup, and examine the roots and supporting structures of each tooth. Based on these findings, a personalized treatment plan is developed.
For mild gingivitis, professional cleaning (scaling) performed by a dental hygienist is often sufficient. However, maintaining regular hygiene appointments, even when gums appear healthy, is essential to prevent recurrence.
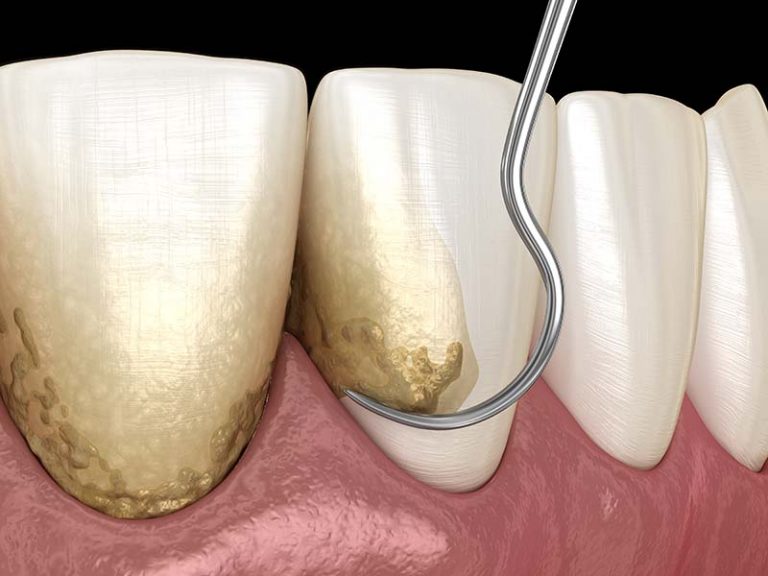
Root Planning: Deep Cleaning for Advanced Cases
When gum disease has progressed beyond the early stages, more thorough treatment is required. Root planning is a deep-cleaning procedure performed by a periodontist, targeting infected tissue and tartar buildup below the gum line.
This process typically involves dividing the mouth into quadrants, with one or two areas treated per session. The procedure removes inflamed tissue and cleans out bacterial deposits from deep gum pockets, helping the gums heal and reattach to the teeth.
Risk Factors That Worsen Gum Disease
Several factors can accelerate the development or progression of gum disease. These include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene - Failure to remove plaque and tartar creates an environment where bacteria thrive.
- Untreated Tartar Buildup - Hardened deposits along the gumline contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Smoking - Tobacco use reduces blood flow to the gums, impairs healing, and increases disease severity.
- Medications - Certain drugs, such as those for blood pressure can influence gum health.
- Stress - High stress levels weaken immune defenses
- Pregnancy - Hormonal create conditions that favor bacterial growth.
- Genetics - A family history of periodontal disease can increase susceptibility.
- Improper Brushing - Brushing too aggressively or inadequately can harm gum tissue or fail to remove plaque effectively.
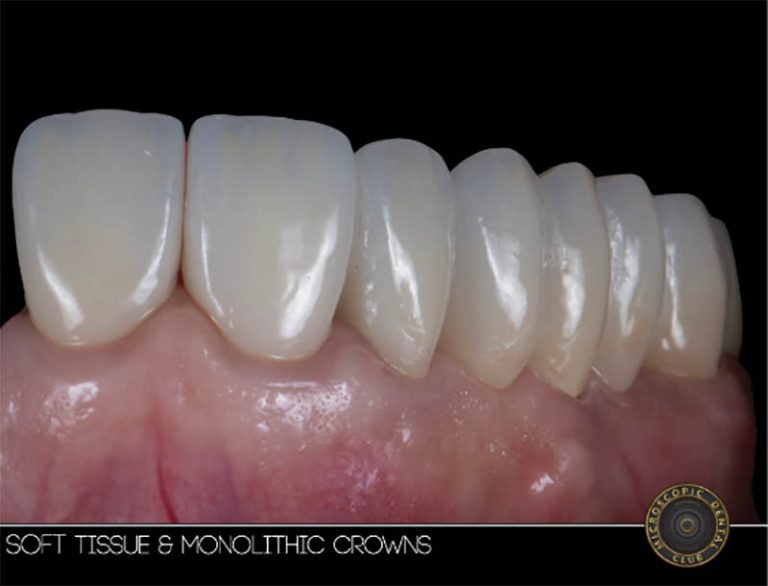
Types of Gum Disease
Gum diseases vary in severity and progression, Additionally, gum disease can develop due to systemic illnesses, severe infections around old root canal treatments, or harmful oral habits.
Type | Description |
Localized Chronic | Involves up to one third of the teeth. |
Generalized Chronic | Affects more than one third of the teeth. |
Aggressive | Rare; usually appears in younger patients, including children and adolescents. |
Localized Aggressive | Damage primarily affects the incisors and molars. |
Generalized Aggressive | Involves widespread inflammatory damage across all teeth. |
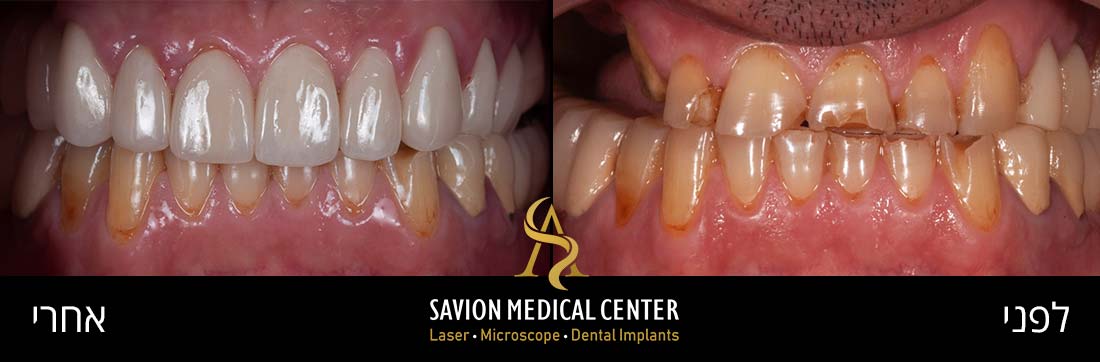
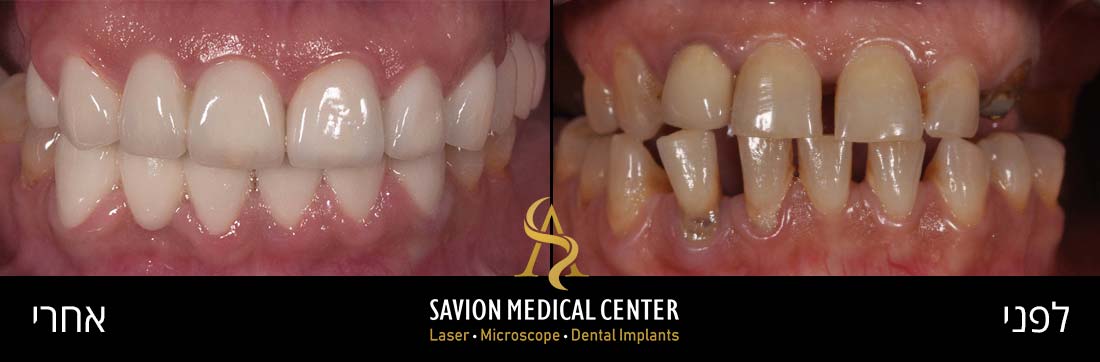
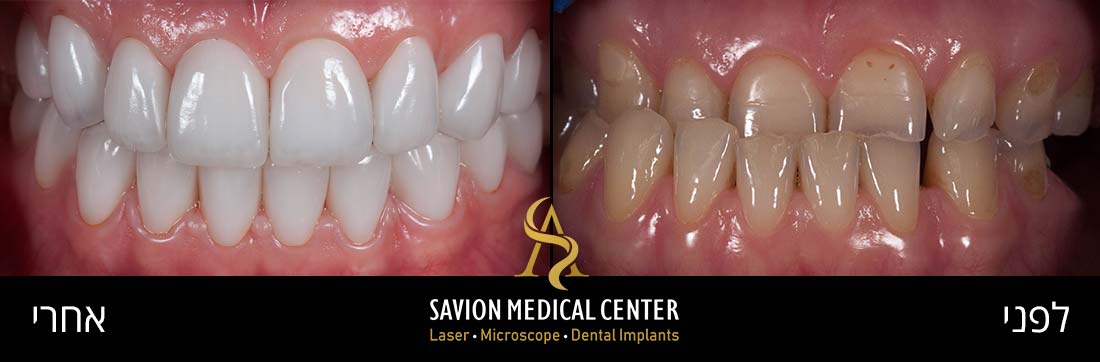
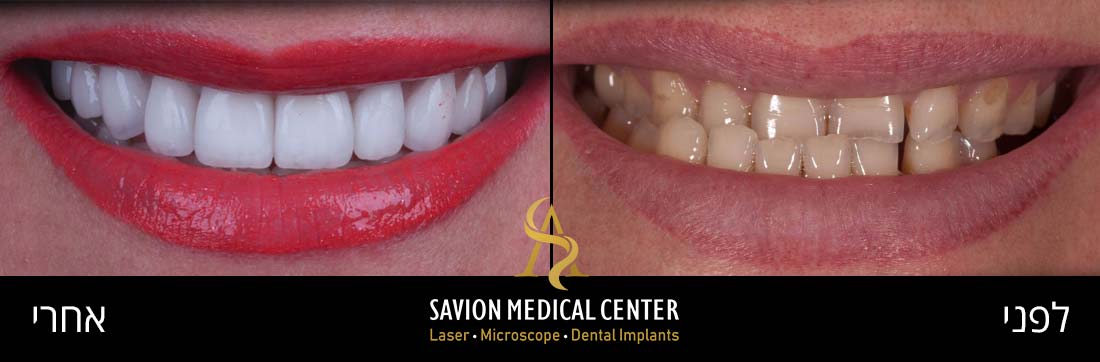
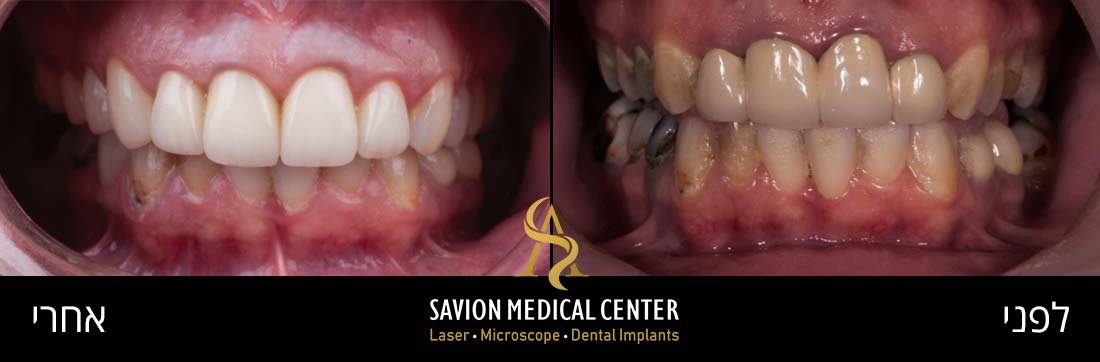
Look at this amazing transformation: From Gum Problems to a Perfect Smile
When Gum Disease Becomes Acute
If left untreated, gum disease can advance into an acute stage, significantly impacting oral health. This stage often includes the formation of gaps between teeth, loosening of teeth, and eventual tooth loss. In severe cases, patients may require restorative treatments such as dental implants to replace lost teeth.
It’s important to note that symptoms may not all appear at once. Even if only a few warning signs are present, they should not be ignored, as early intervention offers the best chance for recovery.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with consistent and proper oral hygiene. Essential steps include:
- Brushing teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing or using interdental cleaners to remove plaque between teeth
- Replacing toothbrushes every three months or sooner if bristles fray
- Using antibacterial mouth rinses as recommended by your dentist
- Scheduling routine check-ups and professional cleanings with your dentist or hygienist
- Correcting defective fillings or crowns that can harbor bacteria and cause irritation

Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
While professional treatment is essential for managing gum disease, certain home remedies can provide temporary relief and support healing. Rinsing with warm salt water helps reduce swelling and discomfort while promoting a cleaner oral environment.
Maintaining proper brushing and flossing habits is also key to preventing bacterial buildup and further irritation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Disease
Mild gingivitis can often improve within a few days to a week following professional cleaning and strict oral hygiene. More advanced or chronic cases, however, may require several weeks or even months of treatment, depending on the extent of tissue damage and the chosen therapy.
Yes. Hormonal changes during pregnancy often make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. Treating gum disease during pregnancy is essential, as untreated inflammation can negatively impact both maternal and fetal health.
While gum disease is rare in children, it does occur. Any sign of bleeding gums, persistent swelling, or discomfort should prompt a visit to a pediatric dentist for a thorough evaluation.
If non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing fail to restore gum health, periodontal surgery may be required. These procedures aim to repair and regenerate gum and bone tissue damaged by advanced disease.
Improperly maintained or ill-fitting crowns and implants can contribute to gum inflammation. In these cases, replacing or adjusting the restorations may be necessary, as determined by your periodontist and restorative dentist.