Introduction:
Bonded porcelain restorations – BPRs, very thin veneer porcelain, or all-ceramic facings, used to improve anterior Aesthetics, and have been available for almost 3 decades. BPRs are placed on top of the tooth after it has undergone minimally invasive preparations, typically limited to enamel. BRPs became popular due to their superior Aesthetic appearance and theirs frequently used in the restorative and prosthetic fields.
Development of new materials and improvements in manufacturing technologies have led clinicians to utilize BPRs in more and more cases.
BPRs achieving patient satisfaction, because of their excellent optical characteristics and biocompatibility. However, these kinds of restorations are usually adhesively cemented, which makes their removal for the purposes of remake, a challenging and time-consuming process.
In conventional way, the veneers removal process performed by cutting and/or grinding off the restoration using rotary burs. The risk of harming the underlying tooth structure due to the lack of color contrast between tooth, adhesive resin interface and the restoration, makes the remake of ceramic restorations a delicate and time-consuming process.
In cases of replacement due to fractures, secondary caries, or gingival recession, the integrity of the veneer following its removal is not important. However, when the removal of the ceramic restoration is required shortly after its insertion because of misalignment during cementation, poor color selection of the luting cement or unexpected inflammatory pulpal responses, keeping the integrity of the restoration becomes critical.
Avoiding the cost involved and the time required for re-manufacturing of the crown or veneer is beneficial for both the clinician and the patient.
With the conventional removal techniques, it is almost impossible to remove the adhesively luted ceramic restoration in one piece.
To overcome these conventional limitations, the use of laser technology was recently introduced as a more comfortable and conservative technique for veneer removal.
The laser-aided ceramic veneers removal has many advantages and several clinical factors may affect it, including chemical composition and type of ceramic, thickness of restoration, resin cement type and shade, ceramic shade and opacity, and laser parameters such as power, pulse duration, frequency and irradiation time.
Medical And Dental Anamnesis:
Patient Motif
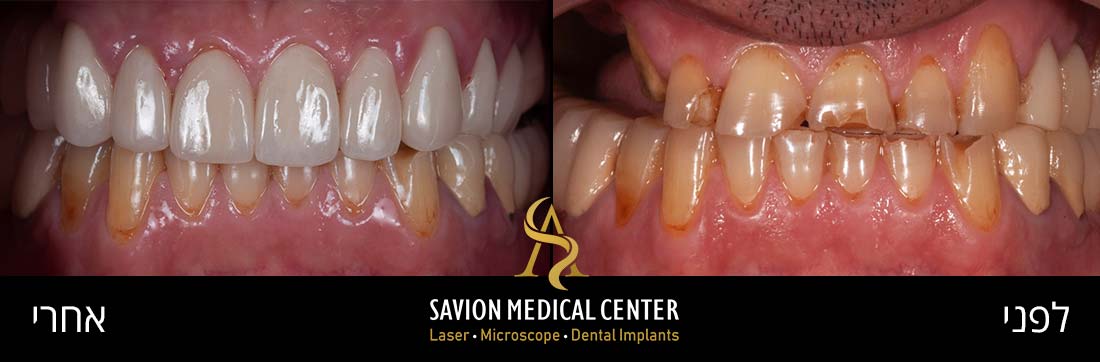
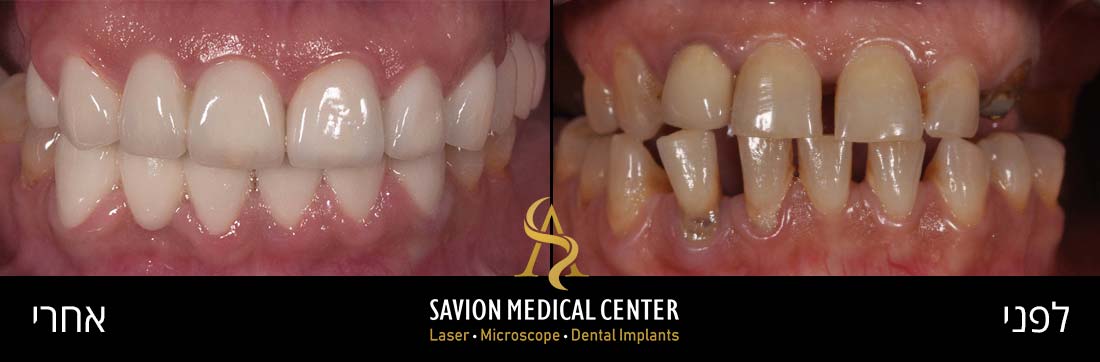
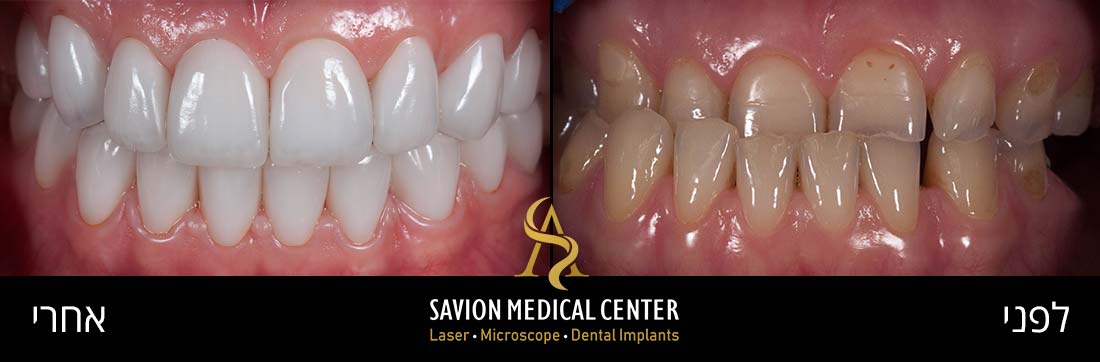
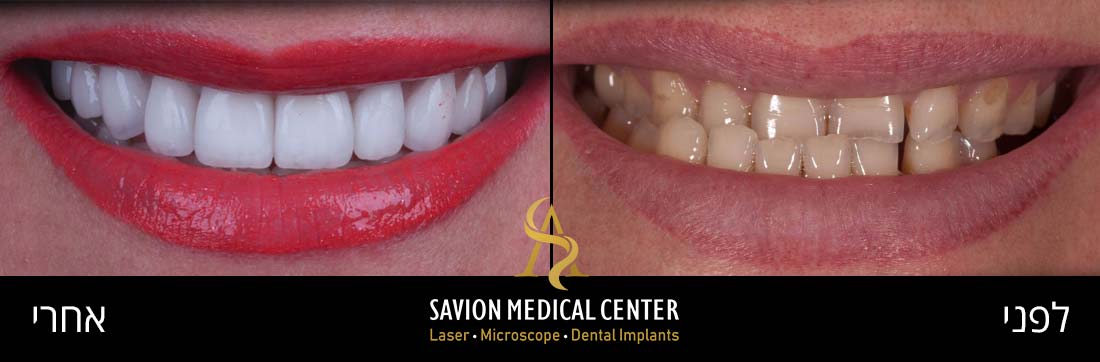
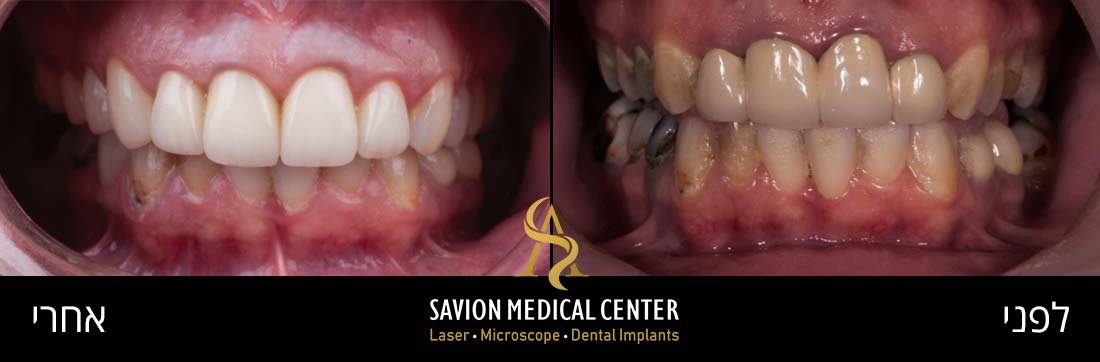
To improve Aesthetic discoloration after first attempt of veneers cementation, patient 55 Y.O Desire whiter and natural appearance.
Clinical Examination
Veneers cemented of 8 upper teeth from 1.4 -2.4. bonded porcelain restorations limited to buco-incisal surface, with veneer thickness of 1 mm approximately. amount of laser transmission through ceramic crowns and veneers is affected by two factors: composition and thickness of the restoration.
Medical History
Patients had no specific local or systemic disease which could affect teeth or gingiva.
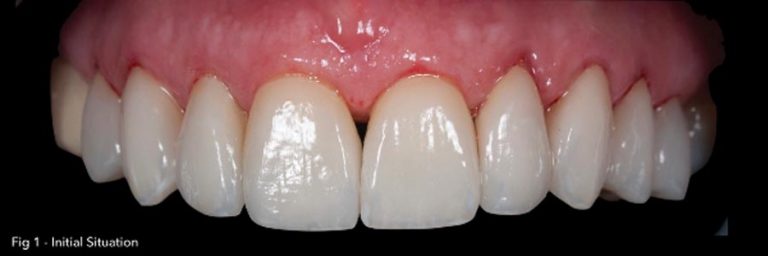
Initial Photography:
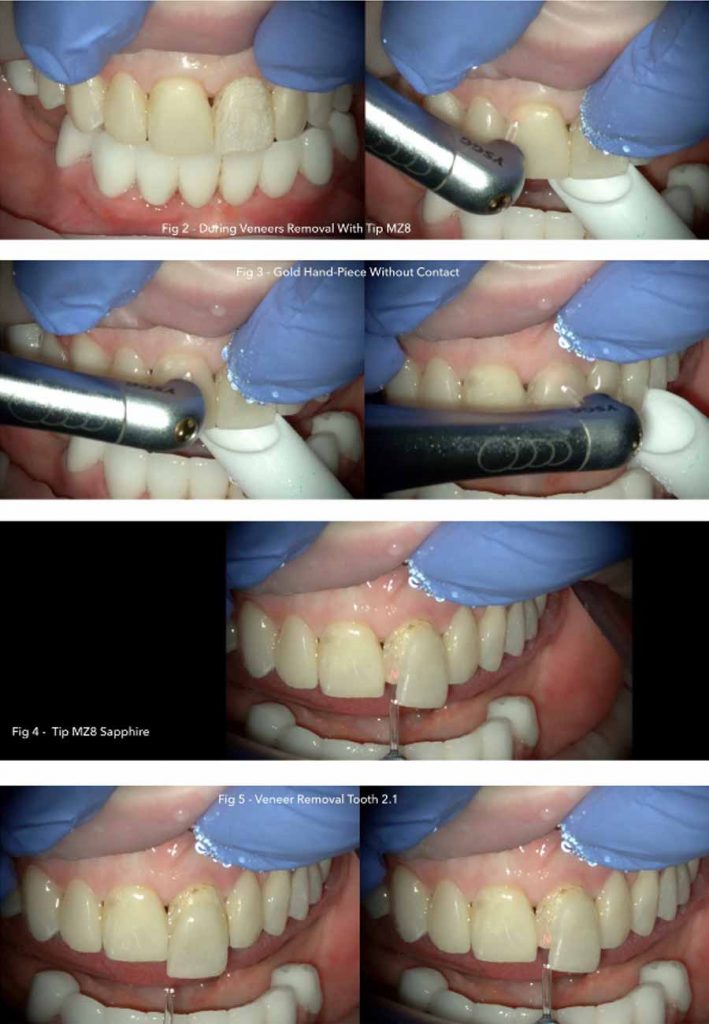
Photography During Procedure:
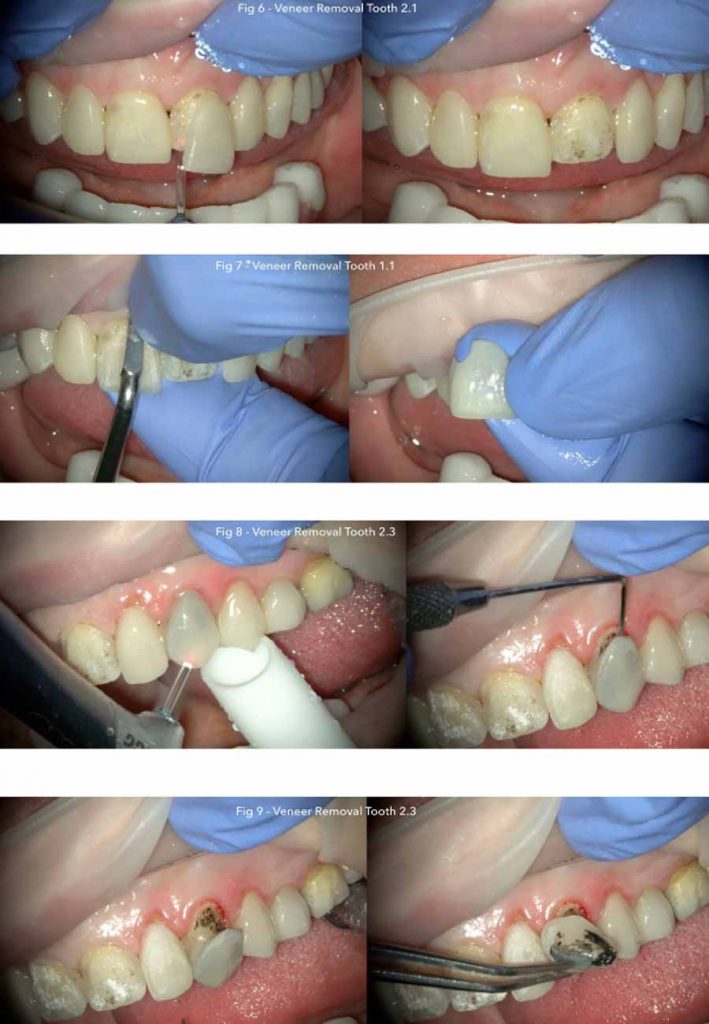
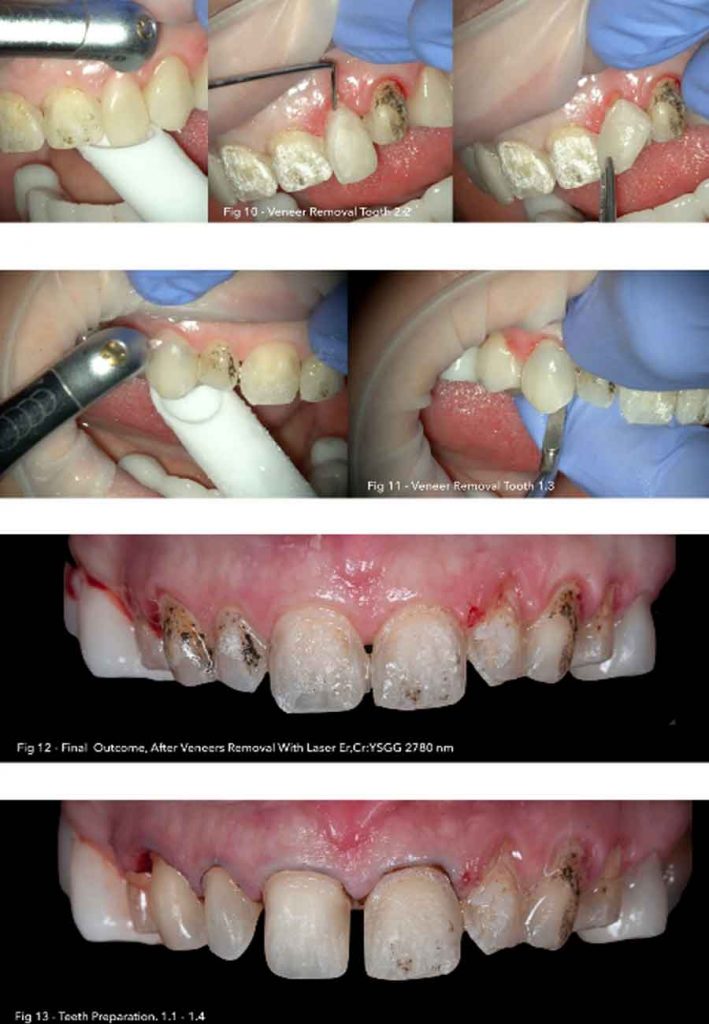
Photograph After Procedure:
Follow Up: Patient did not complain of any pain or discomfort, during surgery or follow up.
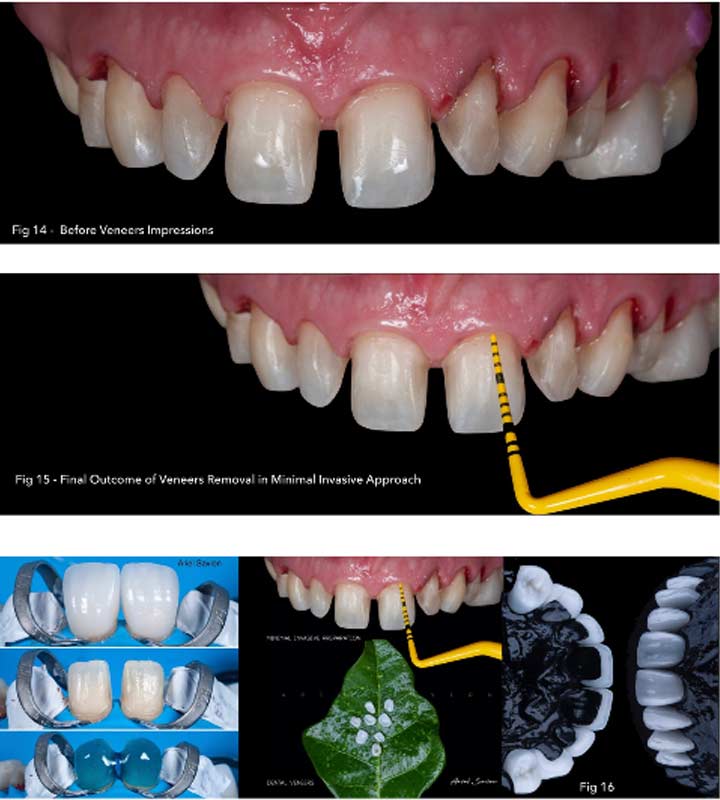
Diagnosis: unaesthetic appearance, diastema between veneers. Patient Wish whiter teeth, complaint about monolithic veneers with chroma without translucency and natural affect of the final outcome.
Aims: The conventional removal procedure is done by grinding these restorations with rotary instruments, although it is time-consuming and inconvenient for the patient and damaging for the dental structure. With laser assisted veneers de-bonding it possible, remove restoration without further iatrogenic damage to underlying tooth.
Laser Parameters: Erbium laser – Erbium, Chromium-doped Yttrium, Scandium, Gallium and Garnet Laser (Er:Cr:YSGG) emission Wavelength of 2780nm. Gold Hand-piece, tip MZ8 – 800μm, Quartz tip, Pulse Duration of 140 μs (H mode), 6.5 W and 20 Hz, water 80%, air 60%.
Treatment: For de-bonding, the Er,Cr:YSGG (2870 nm) laser was positioned perpendicularly at a 2-mm distance from the ceramic veneers and scanning method was performed with horizontal movements parallel to the surface.
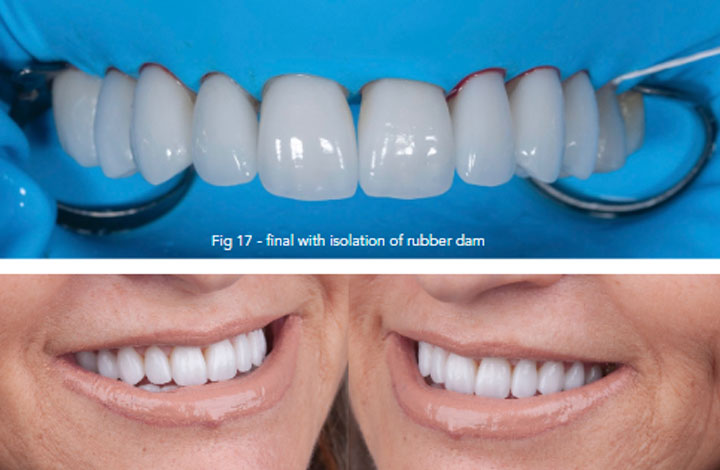
Post Operative Recommendation: no special recommendation was given to the patient after veneers removal with laser.
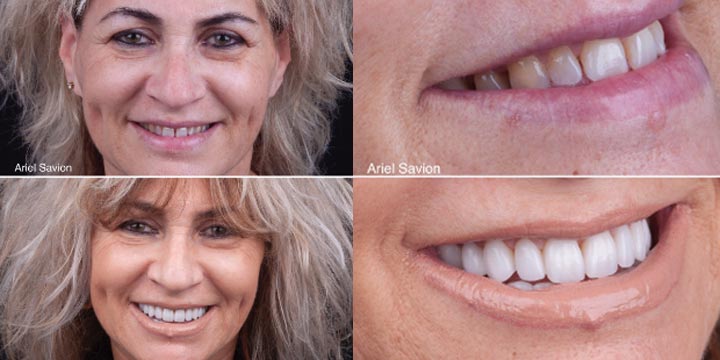
Conclusion: The laser assisted de-bonding procedure in bonded porcelain restorations became easy and safe procedure, comparison to the conventional techniques.
During the de-bonding process of BPRs, erbium laser energy is transmitted through the veneers and is absorbed in the resin cement.
The mechanism of veneer removal using Erbium lasers is mainly based on thermal ablation and photo-ablation of the composite resin cement.
The application of Er,Cr:YSGG was an efficient, fast and safe method for the removal of both feldspathic and lithium reinforced glass ceramic porcelain laminate veneers.